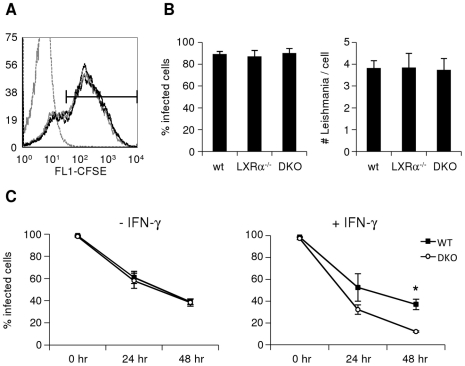
Figure 2. LXR-deficient macrophages are infected similarly, but kill Leishmania more efficiently than wild-type macrophages treated with IFN-γ.
Bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDM) were infected with stationary-phase, (A) CFSE-labeled or (B) unlabelled L. chagasi/infantum at an MOI of 10∶1 for 1 hour, and 2 hours later percentages of infected cells (CFSE-positive events) were determined by (A) flow cytometry (WT uninfected = gray dotted line; WT infected = black solid line; LXRα−/− infected = gray solid line; LXR-DKO infected = black dotted line) or (B) microscopy (the number of parasites per cell was also assessed by microscopy). C. BMDM were infected with stationary-phase, unlabelled L. chagasi/infantum at an MOI of 20∶1 for 2 hours in the presence or absence of IFN-γ (overnight pretreatment), and immediately, 24, or 48 hours later were Giemsa-stained for microscopic quantitation of numbers of amastigotes per cell. Similar results were found in least 3 independent experiments; error bars represent standard error; * denotes p<0.01.