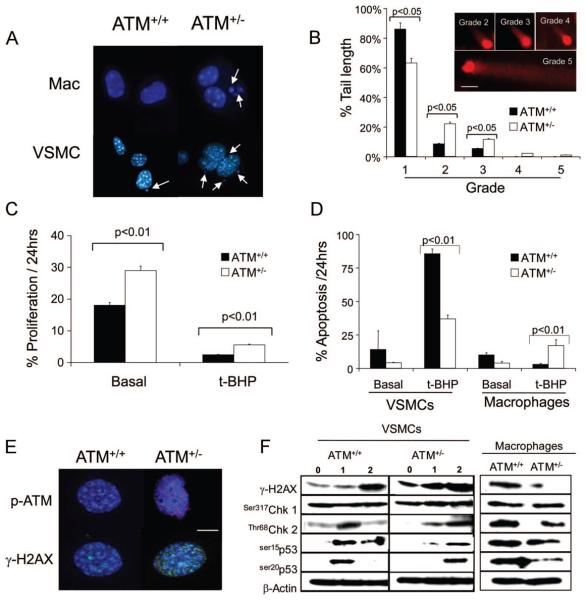
Figure 4. ATM+/− cells demonstrate genomic instability, abnormal cell proliferation, and apoptosis.
A, Micronuclei in macrophages and VSMCs from ATM+/+/ApoE−/− and ATM+/−/ApoE−/− mice (n=3). B, Quantification of DNA comet tails lengths by grade (inset) in ATM+/+/ApoE−/− and ATM+/−/ApoE−/− VSMCs. Cells were incubated for 1 hour with 10 μmol/L t-BHP and comet tails estimated 1 hour later (scale bar=20 μm), n=3. C and D, Percentage of ATM+/+/ApoE−/− and ATM+/−/ApoE−/− VSMCs undergoing proliferation (C) or apoptosis in ATM+/+/ApoE−/− and ATM+/−/ApoE−/− VSMCs and macrophages (D) assessed by time-lapse videomicroscopy over 24 hours, both basally and after exposure to 10 μmol/L t-BHP (n=3). E, Immunocytochemistry of DNA damage foci expression of phospho-ATM (red) and γ-H2AX (green) in ATM+/+/ApoE−/− and ATM+/−/ApoE−/− VSMCs after 10 μmol/L t-BHP for 1 hour and 1-hour recovery. Nuclei are counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar is 20 μm. F, Western blot of ATM+/+/ApoE−/− and ATM+/−/ApoE−/− VSMCs basally (0 hour), after 1 hour of treatment with 10 μmol/L t-BHP (1 hour), and after 1 hour of recovery (2 hours) or ATM+/+/ApoE−/− and ATM+/−/ApoE−/− macrophages after 1 hour of treatment with 10 μmol/L t-BHP and 1 hour of recovery.