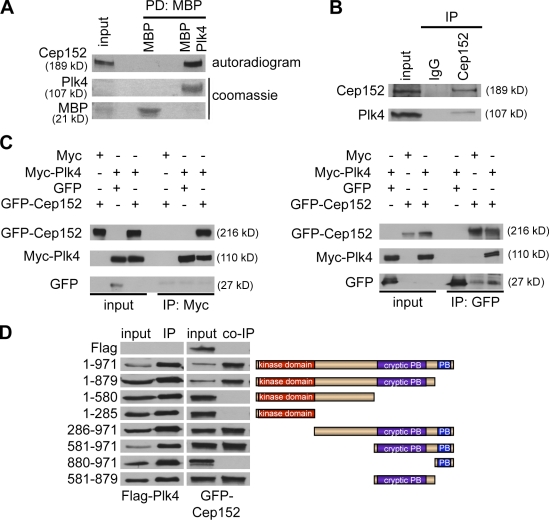
Figure 1.
Cep152 interacts with Plk4 in vitro and in vivo. (A) To analyze in vitro binding between Cep152 and Plk4, either MBP tag alone or MBP-tagged recombinant Plk4 immobilized on amylose beads was used in a binding assay with in vitro–translated [35S]Cep152. Binding of [35S]Cep152 to Plk4 was detected by autoradiography. Equal pull-down of MBP and MBP-Plk4 was shown by Coomassie staining. PD, pull-down. (B) Endogenous Cep152 was immunoprecipitated from U2OS cell extracts using Cep152 (Ab1140). Coprecipitated endogenous Plk4 was detected with a mouse anti-Plk4 antibody by Western blotting. Immunoprecipitation control, random rabbit IgGs. (C) Coimmunoprecipitation of Myc-Plk4 and GFP-Cep152 after coexpression in 293T cells. Reciprocal immunoprecipitation Western blots were performed with anti-Myc and anti-GFP antibodies. Coprecipitated proteins were detected by Western blotting against the corresponding tag. (D, left) Different Flag-Plk4 fragments were coexpressed with GFP-Cep152 in 293T cells. Anti-Flag immunoprecipitates were analyzed in immunoblots for coprecipitated GFP-Cep152 using GFP antibodies. (right) Scheme of expressed Plk4 fragments.