Figure 3. Ato inhibition of oenocyte formation is not due to interference with EGF signaling.
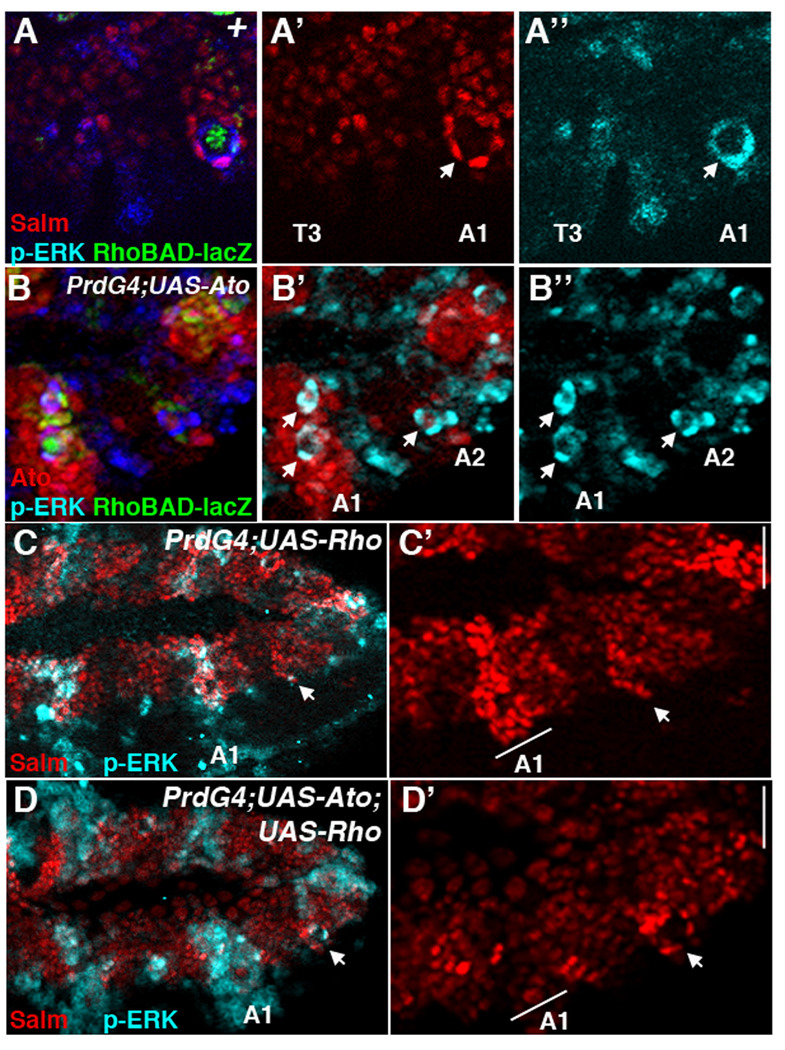
(A-A”) Lateral view of a wild type RhoBAD-lacZ stage 11 embryo showing thoracic (T3) and abdominal (A1) segments immunostained for β-gal (green), Salm (red), and phospho-ERK (blue). β-gal marks the C1 SOP cell that is surrounded by oenocytes (Salm-positive) that co-label with high levels of phospho-ERK. The thorax lacks these cells and significant phospho-ERK activity. (B-B”) Lateral view of a PrdG4; UAS-Ato;RhoBAD-lacZ stage 11 embryo immunostained for Ato (red), β-gal (green), and phospho-ERK (blue). Arrows denote phospho-Erk-positive cell whorls. Note that the first abdominal segment (A1) expresses high levels of Ato and has two visible phospho-ERK-positive cell whorls (arrows). (C–D) Lateral views of stage 11 PrdG4;UAS-Rho stage 11 (C-C’) and PrdG4;UAS-Ato;UAS-Rho stage 11 (D-D’) embryos immunostained for Salm (red) and phospho-ERK (blue). PrdG4 drive Rho expression to activate phospho-ERK in every other segment in both embryos. However, only the PrdG4-on segments expressing rho alone (C-C’) have many cells expressing high levels of Salm. In contrast, the PrdG4-on segments expressing both rho and ato have few cells expressing high levels of Salm. Note, that oenocyte whorls do form in the PrdG4-off segments of both embryos (arrow).
