Abstract
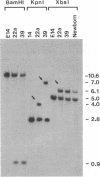
We have inactivated, by gene targeting, the endogenous beta 2-microglobulin gene in a mouse embryonic stem cell line. A cloned fragment of the beta 2-microglobulin gene with the coding sequence disrupted by the insertion of the neomycin-resistance gene was used to transfect the embryonic stem cells. G418-resistant colonies were selected and then screened using the polymerase chain reaction to identify those in which the incoming DNA had integrated into the embryonic stem cell genome by homologous recombination. Of a total of 234 G418-resistant colonies screened, 2 correctly targeted colonies were identified. Chimeric mice carrying the inactivated beta 2-microglobulin gene have been obtained from both of these targeted embryonic cell lines. Breeding of offspring from such animals will allow investigation of the effects of homozygous loss of beta 2-microglobulin.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bjorkman P. J., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bennett W. S., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. The foreign antigen binding site and T cell recognition regions of class I histocompatibility antigens. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):512–518. doi: 10.1038/329512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boggs S. S., Gregg R. G., Borenstein N., Smithies O. Efficient transformation and frequent single-site, single-copy insertion of DNA can be obtained in mouse erythroleukemia cells transformed by electroporation. Exp Hematol. 1986 Nov;14(10):988–994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Linnenbach A., Huebner K., Parnes J. R., Margulies D. H., Appella E., Seidman J. G. Control of expression of histocompatibility antigens (H-2) and beta 2-microglobulin in F9 teratocarcinoma stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5754–5758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doetschman T. C., Eistetter H., Katz M., Schmidt W., Kemler R. The in vitro development of blastocyst-derived embryonic stem cell lines: formation of visceral yolk sac, blood islands and myocardium. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1985 Jun;87:27–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doetschman T., Gregg R. G., Maeda N., Hooper M. L., Melton D. W., Thompson S., Smithies O. Targetted correction of a mutant HPRT gene in mouse embryonic stem cells. Nature. 1987 Dec 10;330(6148):576–578. doi: 10.1038/330576a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. J., Kaufman M. H. Establishment in culture of pluripotential cells from mouse embryos. Nature. 1981 Jul 9;292(5819):154–156. doi: 10.1038/292154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossler A., Doetschman T., Korn R., Serfling E., Kemler R. Transgenesis by means of blastocyst-derived embryonic stem cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9065–9069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper M., Hardy K., Handyside A., Hunter S., Monk M. HPRT-deficient (Lesch-Nyhan) mouse embryos derived from germline colonization by cultured cells. Nature. 1987 Mar 19;326(6110):292–295. doi: 10.1038/326292a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyner A. L., Skarnes W. C., Rossant J. Production of a mutation in mouse En-2 gene by homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells. Nature. 1989 Mar 9;338(6211):153–156. doi: 10.1038/338153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. S., Smithies O. Recombinant fragment assay for gene targetting based on the polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 26;16(18):8887–8903. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.18.8887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller B. H., Hagemann L. J., Doetschman T., Hagaman J. R., Huang S., Williams P. J., First N. L., Maeda N., Smithies O. Germ-line transmission of a planned alteration made in a hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase gene by homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8927–8931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linney E., Donerly S. DNA fragments from F9 PyEC mutants increase expression of heterologous genes in transfected F9 cells. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):693–699. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour S. L., Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Disruption of the proto-oncogene int-2 in mouse embryo-derived stem cells: a general strategy for targeting mutations to non-selectable genes. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):348–352. doi: 10.1038/336348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margulies D. H., Parnes J. R., Johnson N. A., Seidman J. G. Linkage of beta 2-microglobulin and ly-m11 by molecular cloning and DNA-mediated gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2328–2331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozato K., Wan Y. J., Orrison B. M. Mouse major histocompatibility class I gene expression begins at midsomite stage and is inducible in earlier-stage embryos by interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2427–2431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnes J. R., Seidman J. G. Structure of wild-type and mutant mouse beta 2-microglobulin genes. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):661–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90182-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn P., Barros C., Whittingham D. G. Preservation of hamster oocytes to assay the fertilizing capacity of human spermatozoa. J Reprod Fertil. 1982 Sep;66(1):161–168. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0660161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawicki J. A., Magnuson T., Epstein C. J. Evidence for expression of the paternal genome in the two-cell mouse embryo. Nature. 1981 Dec 3;294(5840):450–451. doi: 10.1038/294450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by gene targeting in mouse embryo-derived stem cells. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):503–512. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90646-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S., Clarke A. R., Pow A. M., Hooper M. L., Melton D. W. Germ line transmission and expression of a corrected HPRT gene produced by gene targeting in embryonic stem cells. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):313–321. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90905-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner C. M., Gollnick S. O., Flaherty L., Goldbard S. B. Analysis of Qa-2 antigen expression by preimplantation mouse embryos: possible relationship to the preimplantation-embryo-development (Ped) gene product. Biol Reprod. 1987 Apr;36(3):611–616. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod36.3.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. MHC-restricted cytotoxic T cells: studies on the biological role of polymorphic major transplantation antigens determining T-cell restriction-specificity, function, and responsiveness. Adv Immunol. 1979;27:51–177. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]