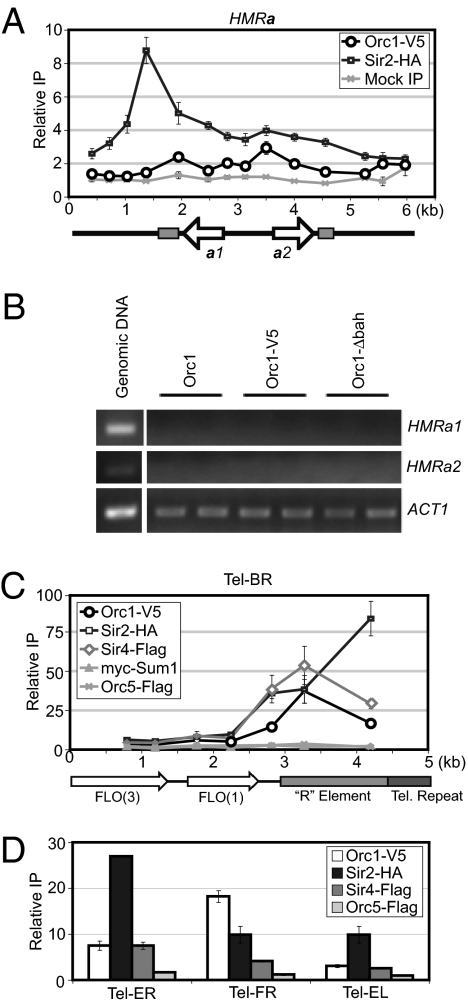
Fig. 4.
KlOrc1 associates with telomeres, but not with HMRa. (A) The associations of KlOrc1–V5 (LRY2581) and KlSir2–HA (LRY2285) with HMRa. A mock precipitation using the V5 antibody was conducted from a strain expressing untagged KlOrc1 (SAY538). Sequences found at HMLα, MAT, and HMRa are represented by light gray boxes. Data for KlSir2–HA were previously reported (15). (B) RT-PCR analysis of HMRa1, HMRa2, and ACT1 in KlOrc1 (SAY538), KlOrc1–V5 (LRY2581) and KlOrc1–Δbah–V5 (LRY2709) strains. (C) The association of KlOrc1–V5 (LRY2561), KlOrc5–Flag (LRY2235), KlSir2–HA (LRY2239), KlSir4–Flag (LRY2239), and myc–KlSum1 (LRY2239) with Tel–BR. Telomeres in K. lactis contain a 1.5- to 2-kb element, termed the R element, immediately adjacent to the telomeric repeat (58). The R element, as well as the telomeric repeat sequence and the ORFs FLO3 and FLO1 are indicated. (D) Association of KlOrc1–V5, KlOrc5–Flag, KlSir2–HA, and KlSir4–Flag with Tel–ER, Tel–FR, and Tel–EL was assessed using the same chromatin IP samples as in C.