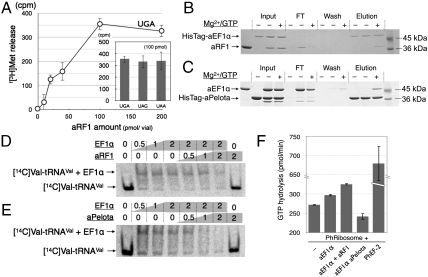
Fig. 2.
In vitro analysis of aRF1 and Pelota for aEF1α binding. (A) The f[3H]Met release assay of aRF1, using HeLa S3 ribosomes programmed with a stop-codon containing mini mRNA. The dose curve for UGA-dependent release and the activities at 100 pmol/50-μL reaction volume are shown in the histogram. The in vitro binding of HisTagged-aEF1α to aRF1 (B) and the in vitro binding of HisTagged-aPelota to aEF1α (C) are demonstrated by pull-down assays. The reaction mixtures including the factors [“Input,” HisTagged protein only (Left), HisTagged protein and nontagged protein (Middle), both with Mg2+/GTP (Right)] were mixed with MagneHis™ Ni particles and the HisTagged proteins were immobilized, and then the HisTagged proteins and their binding factors were resolved by SDS-PAGE. The flow-through fraction (FT), the wash fractions (Wash), and the eluted fractions (“Elution”) are shown. In vitro competition assays for the aEF1α-[14C]Valyl-tRNAVal complex by aRF1 (D) and aPelota (E) are shown. The mixtures of [14C]Valyl-tRNAVal with the factors indicated above were resolved by native PAGE, and the shifted bands were analyzed. (F) GTPase assay with Pyrococcus ribosomes. The ribosomes were mixed with various combinations of aEF1α (10 pmol), aRF1 (40 pmol), and aPelota (40 pmol), or with Ph EF-2 (10 pmol, as a control of GTP hydrolysis by translational GTPase in Pyrococcus horikoshii ribosomes), as indicated. See Materials and Methods for details.