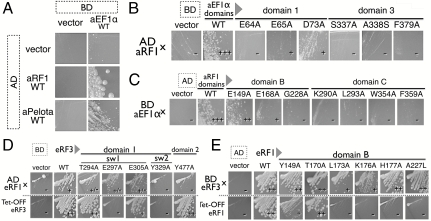
Fig. 4.
Yeast two-hybrid analysis of aRF1/Pelota binding to aEF1α at sites 1 and 2. (A) Two-hybrid analysis (5-d growth) between wild-type aEF1α (binding domain, BD) and aRF1/aPelota (activation domain, AD). (B) Two-hybrid analysis (3-d growth) of mutants on site 1 and site 2 residues in aEF1α (BD) against aRF1 wild type (AD). (C) Two-hybrid analysis (3-d growth) on mutants of site 1 and site 2 residues in aRF1 (AD) against aEF1α wild type (BD). (D) Mutational analysis of site 2 residues in Sp-eRF3. The upper row presents the results of the two-hybrid interaction of Sp-eRF3 mutants (BD) against Sp-eRF1ΔN2-F288A (AD). The lower row presents the results of the complementation of Tet-off eRF3 S. cerevisiae strain. (E) Mutational analysis on site 2 residues in SP-eRF1. The upper row presents the results of the two-hybrid interaction of Sp-eRF1 mutants (AD) against Sp-eRF3-Y577A (BD). The lower row presents the results of the complementation of Tet-off eRF1 S. cerevisiae strain.