Figure 4.
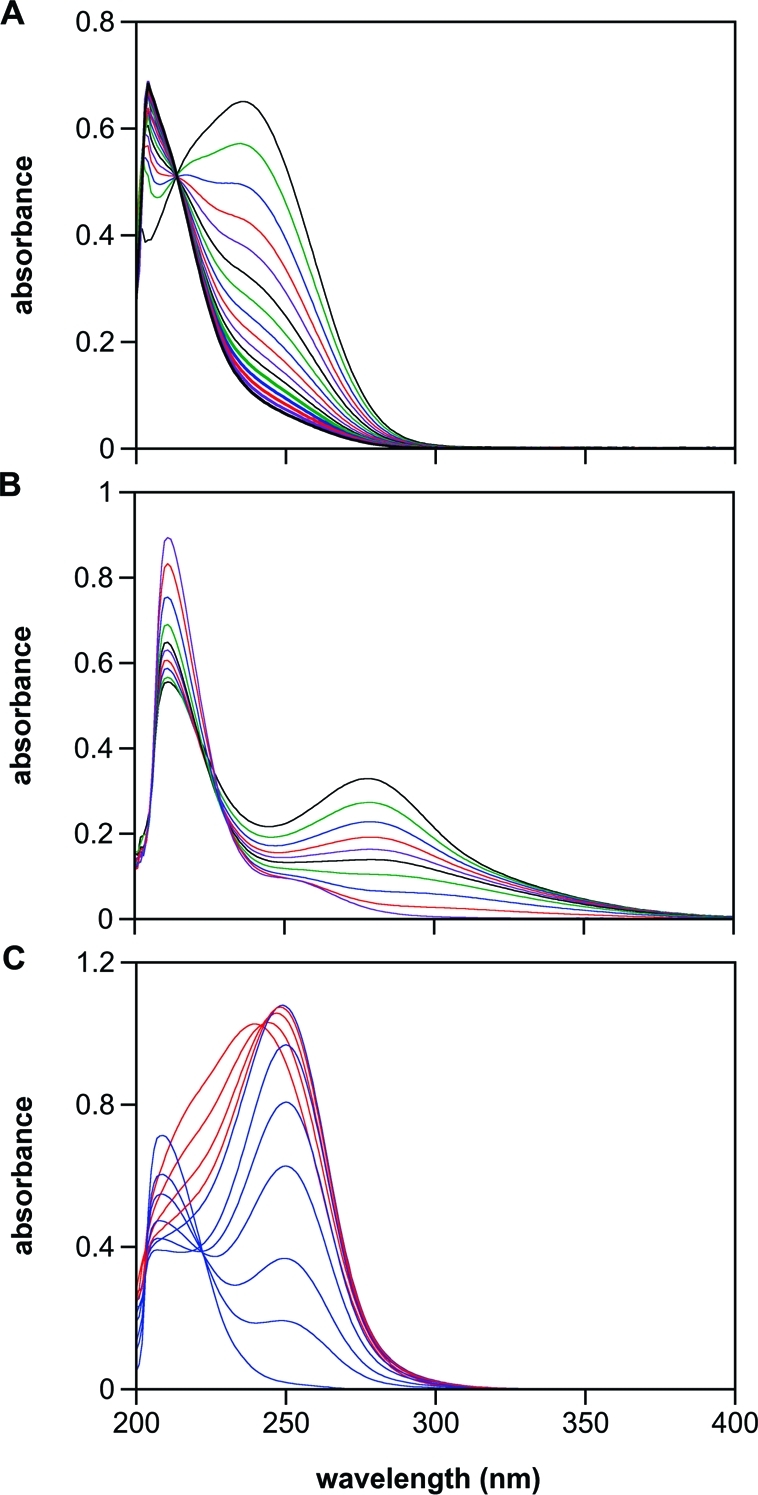
Spontaneous (A and B), and esterase-catalyzed (C) hydrolysis, of 2. In panel A, spectra were collected every 60 s (10-min intervals shown) after dissolving 2 in PBS (pH 7.4) at 37 °C, and only loss of the parent compound was observed. In panel B, the pH was elevated to 12, and scans were collected every 0.5 s (through 2.5 s and 3.5, 5.5, 9.5, and 54.5 s shown). In panel C, porcine liver esterase (1.4 U/mL) was added (pH 7.4), and spectra were collected every 10 s. Hydrolysis of 2 (λmax 236 nm) to 1 (λmax 250 nm) was complete within 40 s (0.067 s−1; red spectra) under these conditions. The rate of decay of 1 in panel C (blue spectra at 40, 100, 160, 240, 400, 600, and 2460 s) was comparable to that shown in Figure 3A (0.0033 s−1 vs 0.0012 s−1, respectively). Elevation of the intensity near 200 nm indicates formation of autoxidation products such as nitrite. Deaeration inhibited this peak (data not shown).
