Abstract
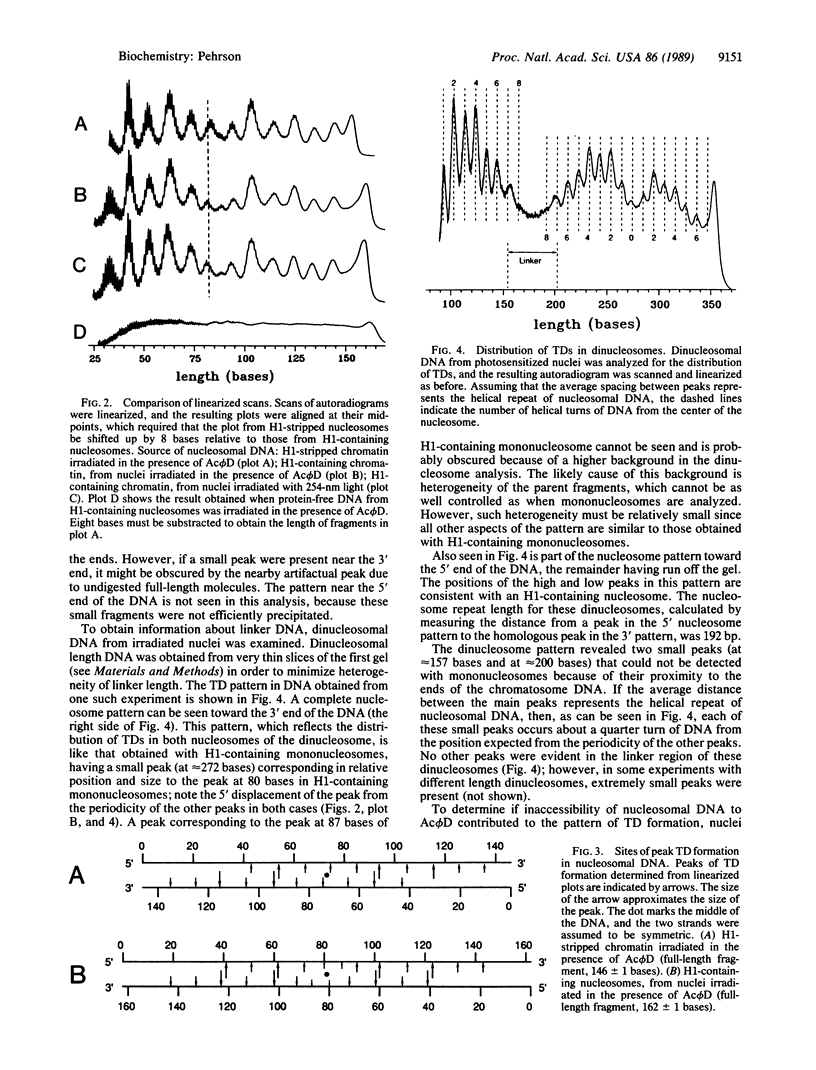
Photo-induced thymine dimer formation was used to probe nucleosome structure in nuclei. The distribution of thymine dimers in the nucleosome and recent studies of the structure of thymine dimer-containing DNA suggest that the rate of thymine dimer formation is affected by the direction and degree of DNA bending. This premise was used to construct a model of the path of DNA in the nucleosome, which has the following features. (i) There are four regions of sharp bending, two which have been seen previously by x-ray crystallography of the core particle. (ii) The DNA in H1-containing nucleosomes deviates from its superhelical path near the midpoint; this is not seen with H1-stripped chromatin. (iii) The internucleosomal (linker) DNA appears to be relatively straight.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crothers D. M., Dattagupta N., Hogan M., Klevan L., Lee K. S. Transient electric dichroism studies of nucleosomal particles. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 17;17(21):4525–4533. doi: 10.1021/bi00614a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doetsch P. W., Chan G. L., Haseltine W. A. T4 DNA polymerase (3'-5') exonuclease, an enzyme for the detection and quantitation of stable DNA lesions: the ultraviolet light example. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 10;13(9):3285–3304. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.9.3285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale J. M., Nissen K. A., Smerdon M. J. UV-induced formation of pyrimidine dimers in nucleosome core DNA is strongly modulated with a period of 10.3 bases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6644–6648. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale J. M., Smerdon M. J. Photofootprint of nucleosome core DNA in intact chromatin having different structural states. J Mol Biol. 1988 Dec 20;204(4):949–958. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90054-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale J. M., Smerdon M. J. UV-induced pyrimidine dimers and trimethylpsoralen cross-links do not alter chromatin folding in vitro. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 20;27(19):7197–7205. doi: 10.1021/bi00419a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan M. E., Rooney T. F., Austin R. H. Evidence for kinks in DNA folding in the nucleosome. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):554–557. doi: 10.1038/328554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain I., Griffith J., Sancar A. Thymine dimers bend DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2558–2562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutter L. C. Precise location of DNase I cutting sites in the nucleosome core determined by high resolution gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jan;6(1):41–56. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Felsenfeld G. Reaction of nucleosome DNA with dimethyl sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2133–2137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Felsenfeld G. Reconstitution of nucleosome core particles containing glucosylated DNA. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 15;158(4):685–698. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90254-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meistrich M. L., Lamola A. A., Gabbay E. Sensitized photoinactivation of bacteriophage T4. Photochem Photobiol. 1970 Mar;11(3):169–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1970.tb05985.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meistrich M. L., Lamola A. A. Triplet-state sensitization of thymine photodimerization in bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1972 Apr 28;66(1):83–95. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(72)80007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitra S., Sen D., Crothers D. M. Orientation of nucleosomes and linker DNA in calf thymus chromatin determined by photochemical dichroism. Nature. 1984 Mar 15;308(5956):247–250. doi: 10.1038/308247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M., Kornberg R. D. Action of micrococcal nuclease on chromatin and the location of histone H1. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jan 25;109(3):393–404. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlman D. A., Holbrook S. R., Pirkle D. H., Kim S. H. Molecular models for DNA damaged by photoreaction. Science. 1985 Mar 15;227(4692):1304–1308. doi: 10.1126/science.3975615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pehrson J. R., Cohen L. H. Embryonal histone H1 subtypes of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus: purification, characterization, and immunological comparison with H1 subtypes of the adult. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6761–6764. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond T. J., Finch J. T., Rushton B., Rhodes D., Klug A. Structure of the nucleosome core particle at 7 A resolution. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):532–537. doi: 10.1038/311532a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond T. J., Searles M. A., Simpson R. T. Crystals of a nucleosome core particle containing defined sequence DNA. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 5;199(1):161–170. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90386-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose S. M., Garrard W. T. Differentiation-dependent chromatin alterations precede and accompany transcription of immunoglobulin light chain genes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8534–8544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satchwell S. C., Drew H. R., Travers A. A. Sequence periodicities in chicken nucleosome core DNA. J Mol Biol. 1986 Oct 20;191(4):659–675. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90452-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T. Structure of the chromatosome, a chromatin particle containing 160 base pairs of DNA and all the histones. Biochemistry. 1978 Dec 12;17(25):5524–5531. doi: 10.1021/bi00618a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spadafora C., Oudet P., Chambon P. Rearrangement of chromatin structure induced by increasing ionic strength and temperature. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct;100(1):225–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb02053.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss F., Prunell A. Nucleosome spacing in rat liver chromatin. A study with exonuclease III. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 10;10(7):2275–2293. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.7.2275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. F., Smerdon M. J. Nucleosome rearrangement in vitro. 1. Two phases of salt-induced nucleosome migration in nuclei. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 3;24(25):7279–7287. doi: 10.1021/bi00346a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]