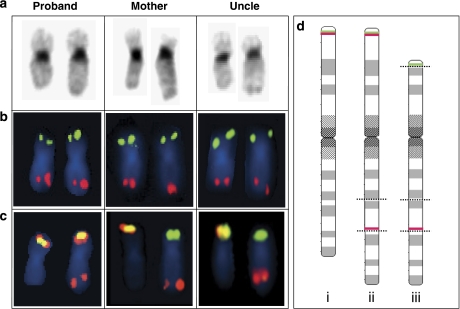
Figure 4.
G-banding ( a) and FISH analyses (b and c) of the proband, her mother and the maternal uncle. In all panels, the normal chromosome 19 is on the left. The proband has a 19q arm that is too long, reflecting her inheritance of a recombinant chromosome 19 from her mother with a p13.2p13.3 insertion into 19q13 combined with a normal 19p arm. The mother and uncle both have a balanced pericentric insertion. In panel b, the subtelomere chromosome 19 FISH results are shown, giving normal signals in all the examined individuals. In panel c, the TCF3 FISH result is shown. The TCF3 FISH split signal probe normally produces a yellow fusion signal at 19p. In the proband, this signal is found in addition to a red signal on 19q, representing the centromeric part of the TCF3 probe. In the mother and uncle, the presence of TCF3 at the distal duplication breakpoint results in the absence of a normal yellow fusion signal. (d) The three different types of chromosome 19 found in this family are shown, illustrated by 850-band level ideograms: (i) a normal chromosome 19; (ii) chromosome 19 with an unbalanced pericentric insertion, as detected in the proband; (iii) chromosome 19 with a balanced 19p13.2p13.3-into-19q13.3 pericentric insertion, as detected in the mother and uncle. The positions of the breakpoints are marked with dotted lines. Also, the positions of the detected TCF3 FISH probe signals are indicated by green lines (the telomeric TCF3 probe) and red lines (the centromeric TCF3 probe).