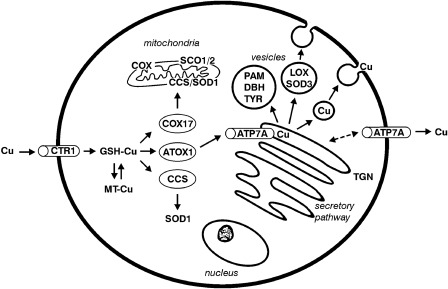
Figure 4.
Schematic illustration of cellular copper transport. Copper is taken up across the plasma membrane by the copper uptake transporter (CTR1) as cuprous ions (CuI). Within the cytoplasma, the copper is found attached to glutathione (GSH), metallothionein (MT), or copper chaperons, which deliver copper to enzymes and compartments. COX17 is the copper chaperone for COX, CCS is the copper chaperone for the cytoplasmic superoxide dismutase (SOD1), and HAH1 is the copper chaperone for ATP7A, which delivers copper to peptidyl-α-amidating enzyme (PAM), dopamine β-hydroxylase (DBH), tyrosinase (TYR), lysyl oxidase (LOX), and extracellular SOD3. ATP7A is also responsible for copper export from cells. At low copper concentrations, the localization of the protein is at the TGN, but at high copper concentrations it will be relocated to the plasma membrane. In the liver the role of ATP7A is performed by ATP7B.