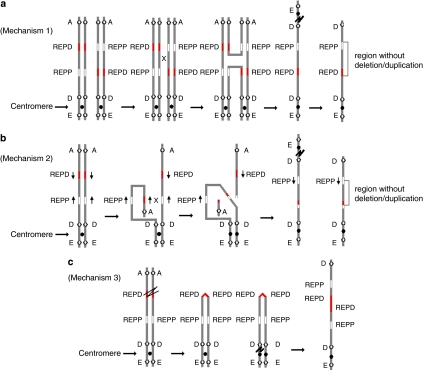
Figure 3.
(a) Mechanism 1 in which the chromosome carrying the paracentric inversion between REPD and REPP pairs with its homologue by forming an inversion loop. Crossing-over and recombination within the loop create an unstable dicentric chromosome and an acentric fragment. The dicentric chromosome breaks outside the inverted region lead to the formation of a monocentric chromosome with a terminal deletion and an inverted duplication with a single copy region between the duplication. (b) Mechanism 2 in which the inverted LCRs within REPD or REPP in the same short arm of chromosome 8. Pairing and recombination between the inverted repeats on sister chromatids results in the formation of a dicentric chromosome and an acentric fragment. Breakage of the dicentric outside the inverted repeats leads to a monocentric chromosome with a terminal deletion and an inverted duplication with a single copy region between the duplication, which will be flanked by the inverted repeats. (c) Mechanism 3, which involves an initial premeiotic double-strand break of the two sister chromatids. Fusion of the broken ends results in a symmetric U-type reunion between the sister chromatids leading to the formation of a dicentric chromosome. Breakage distal to the fusion site outside the fusion region results in a monocentric chromosome with a terminal deletion and an inverted duplication without a single copy region between the duplication.