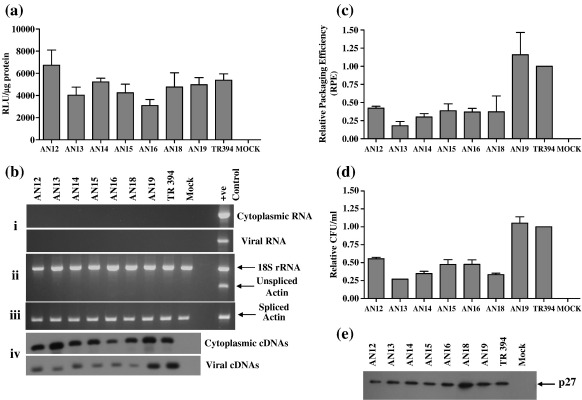
Fig. 2.
Role of the complementary heptanucleotides in R/U5 and Gag involved in LRI towards FIV RNA packaging and propagation. (a) Transfection efficiency of mutants and wild type transfer vector as assessed by the firefly luciferase activity from the co-transfected pGL3 control DNA using the dual luciferase assay kit. RLU, relative light units. The average of the data from three independent representative experiments is shown. (b) RT-PCR of viral and cytoplasmic RNA fractions with appropriate controls. (i) Amplification of the DNase-treated cytoplasmic (upper panel) and viral (lower panel) RNA preparations using transfer vector specific primers. (ii) and (iii) Controls for the nucleocytoplasmic fractionation technique; (ii) amplification of unspliced β-actin mRNA and 18S rRNA; (iii) amplification of spliced β-actin mRNA. (iv) Representative Southern blot of the amplified products following RT-PCR that was conducted on transfer vector cytoplasmic cDNAs (upper panel) and viral cDNAs (lower panel) using vector-specific primers. (c) Relative packaging efficiency (RPE) of transfer vector RNAs. As described in Materials and Methods, the amount of genomic RNA packaged for each mutant was compared with the wild type (TR394) after quantification of the bands obtained following semi-quantitative RT-PCR. (d) Relative hygromycin-resistant (Hygr) colony-forming unit (CFU)/ml for mutant transfer vectors reflecting the relative RNA propagation efficiencies. The CFU/ml value expressed for each mutant is relative to the wild type (TR394) and data were derived after normalization to the transfection efficiencies. (e) Representative western blot conducted on the pelleted viral particles. The RPE and relative CFU data represent the mean of at least three independent transfection and infection experiments testing all mutants except for the relative CFU/ml value of AN13. RLU, relative light units/μg of protein.