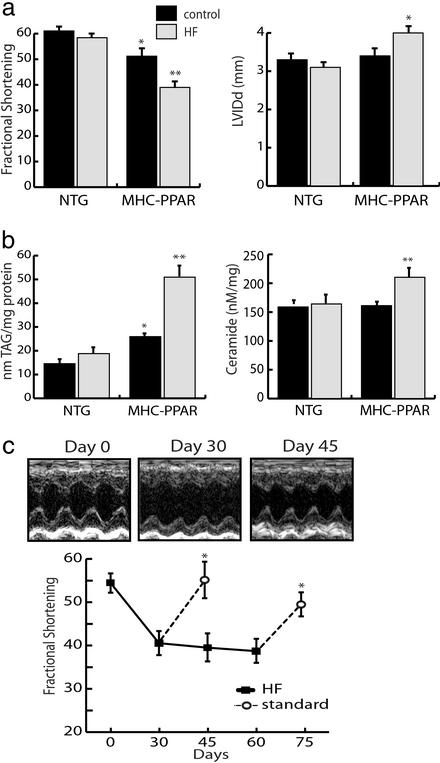
Figure 3.
The cardiomyopathy of MHC-PPAR mice is worsened by consumption of a diet rich in LCFA. (a) Bars represent mean LV FS (Left) and LV internal diameter at diastole (LVIDd, Right) of NTG and MHC-PPAR (404-4 line) mice on HF chow rich in LCFA or calorie-matched control chow. (b) TAG and ceramide levels in hearts of NTG and MHC-PPAR mice after HF diet treatment, as determined by ESIMS. Bars represent mean levels of long-chain TAG (Left) and ceramide (Right). *, P < 0.05 vs. NTG mice. **, P < 0.05 vs. NTG mice and control chow-fed MHC-PPAR mice. (c) HF diet-induced ventricular dysfunction in MHC-PPAR mice is reversible. The graph displays mean FS of MHC-PPAR mice plotted as a function of time. Black squares represent transgenic mice fed the HF diet. Subgroups of mice returned to a standard rodent chow for 15 days at the 30th and 60th days of the trial are denoted by the white circles. *, P < 0.05 vs. corresponding HF-fed MHC-PPAR mice. (Upper) M-mode echocardiographic images of the LV of a representative MHC-PPAR mouse at baseline (Day 0), after 30 days on the HF diet (Day 30) and 15 days after being returned to the standard chow (Day 45).