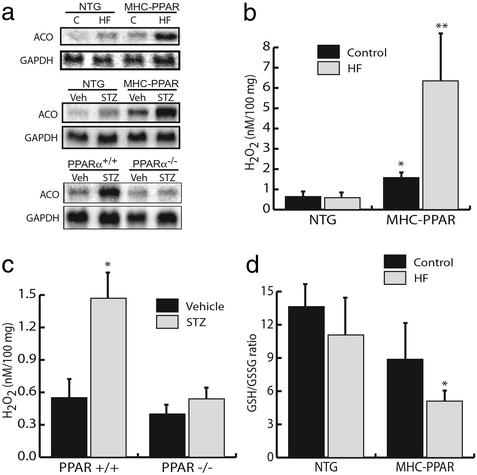
Figure 5.
Activation of extra-mitochondrial lipid metabolic pathways correlates with the severity of the cardiomyopathic phenotype. (a) HF diet or STZ treatment activates the peroxisomal FAO pathway in a PPARα-dependent manner. Representative autoradiographs of Northern blot analyses performed with total RNA isolated from cardiac ventricle of NTG or MHC-PPAR mice after 4 weeks of HF or control (C) diet (Top), NTG or MHC-PPAR mice 6 weeks after STZ administration (Middle), PPARα+/+ and PPARα−/− mice 5 days after vehicle or STZ injection (Bottom) using cDNA probes denoted at left. (b) Bars represent mean hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) levels in cardiac extracts from NTG or MHC-PPAR mice after 4 weeks of HF diet. *, P < 0.05 vs. NTG mice. **, P < 0.05 vs. NTG mice and MHC-PPAR mice fed control chow. (c) PPARα is required for the generation of H2O2 in the diabetic heart. Bars represent mean H2O2 levels in cardiac extracts isolated from PPARα+/+ and PPARα−/− mice 5 days after an injection of vehicle or STZ. *, P < 0.05 vs. vehicle-injected wild-type and all PPARα-null mice. (d) Bars represent mean GSH/GSSG ratios (n ≥ 4) in cardiac extracts from MHC-PPAR mice after 4 weeks of control or HF diet. *, P < 0.05 vs. NTG mice given HF chow.