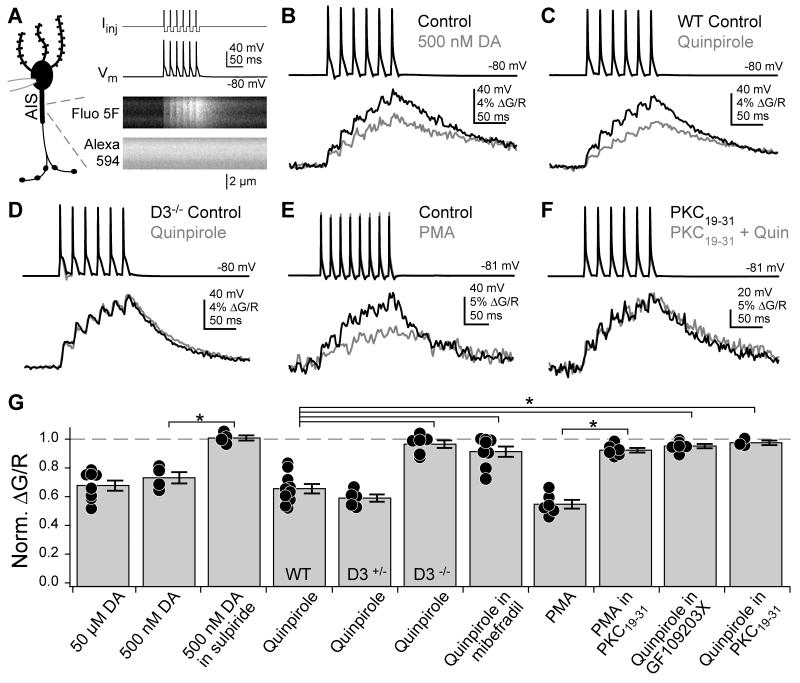
Fig. 1. Dopamine reduces AIS Ca2+ transients in cartwheel cells.
(A) Left: Schematic of recording/imaging configuration. Whole-cell recordings were made from cartwheel cell somata, and Ca2+ transients were imaged in the AIS. Top right: AP trains were evoked by somatic current injection followed by negative current steps to ensure that only 1 AP was evoked per step. Bottom right: corresponding Fluo-5F (Ca2+) and Alexa 594 (morphology) signals in AIS. (B-F) AP train-evoked Ca2+ influx in the AIS. Shades correspond to drug conditions to right of AP trains. All Ca2+ transients were computed as the change in green fluorescence (G, Fluo-5F) over red fluorescence (R, Alexa). DA: dopamine. WT: wild type.
(G) Summary of pharmacological effects on AIS Ca2+. Values normalized to baseline ΔG/R amplitudes. For conditions expressed as “Drug X in Drug Y”, normalized ΔG/R amplitudes reflect any changes mediated by Drug X relative to a baseline period in Drug Y. Dots are single cells. Error bars are SEM. Asterisk: p < 0.0001.