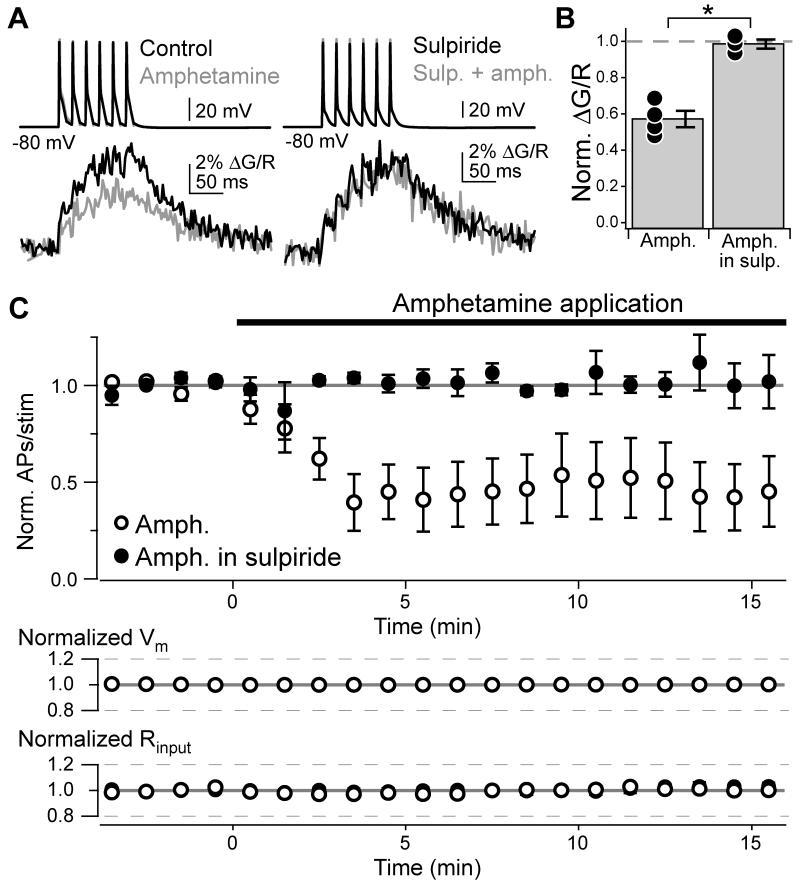
Fig. 7. Amphetamine reduces AIS Ca2+ and spike output.
(A) AP train-evoked Ca2+ influx in the AIS, imaged with Fluo-5F. Colors correspond to drug conditions to right of AP trains.
(B) Summary of amphetamine effects on AIS Ca2+. Dots are single cells. Bars are SEM. Asterisk: p < 0.05.
(C) Time course of AP inhibition by amphetamine. When required, sulpiride was present throughout the recording. Data normalized to baseline number of APs evoked per stimulus. Bars are SEM.