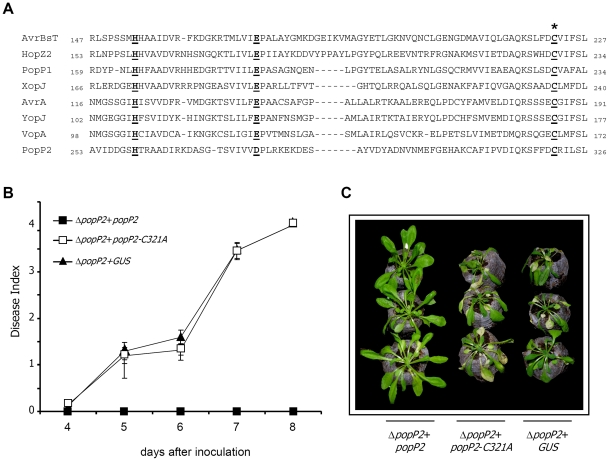
Figure 1. Mutation of cysteine 321 in PopP2 leads to loss of PopP2-triggered immunity on RRS1-R expressing plants.
A: Sequence alignment of representative members of the YopJ-like effector family from plant and animal bacterial pathogens showing the conserved catalytic triad. Conserved residues in the catalytic core (H, D/E, C) are underlined and shown in bold. The star indicates the position of the main cysteine catalytic residue. Accession numbers for the proteins are: Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria AvrBsT (AAD39255); Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae HopZ2 (ABK13722); R. solanacearum PopP1 (CAF32331) and PopP2 (CAD14570); Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria XopJ (YP_363887); Salmonella enterica AvrA (AAB83970); Yersinia pestis YopJ (NP_395205); and Vibrio parahaemolyticus VopA (AAT08443). B: Disease symptom development curves. Individual Nd-1 (RRS1-R) Arabidopsis plants were scored 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8 days after inoculation R. solanacearum ΔpopP2 strain expressing wild-type PopP2 (black squares), PopP2-C321A (white squares) or a GUS control (black triangles), using the following scale: 0 = no wilting, 1 = 25%, 2 = 50%, 3 = 75%, and 4 = 100% of wilted leaves. Mean and SD values were calculated from scores of a total of 40 plants (from three independent experiments). C: Phenotypic responses of Nd-1 (RRS1-R) Arabidopsis plants 8 days after inoculation with the indicated bacterial strains.