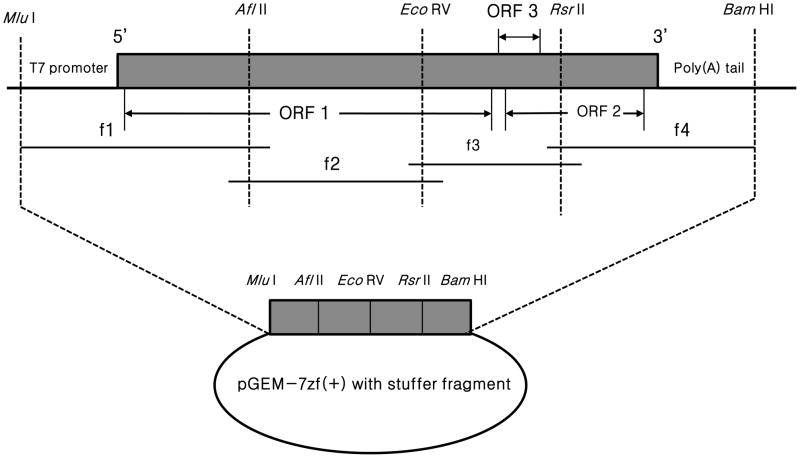
Fig. 1.
A schematic diagram of the strategies used to assemble the full-length cDNA clone of avian HEV-VA strain originally isolated from a healthy chicken in Virginia. The genome organization of the avian HEV-VA and the positions of the unique restriction enzyme sites used for cloning purposes are indicated. The complete genome of avian HEV-VA is amplified by four overlapping fragments (f 1 to 4) flanked by unique restriction enzyme sites. An Mlu I site and a T7 core promoter sequence were engineered at the 5′ end of the f1 fragment. A stretch of 18 adenosines and Bam HI sites were introduced at the 3′ end of the viral genome (f 4 fragment). The 4 overlapping fragments were individually cloned into the pGEM-7z(+) vector that contains an engineered stuffer fragment with unique restriction enzyme sites.