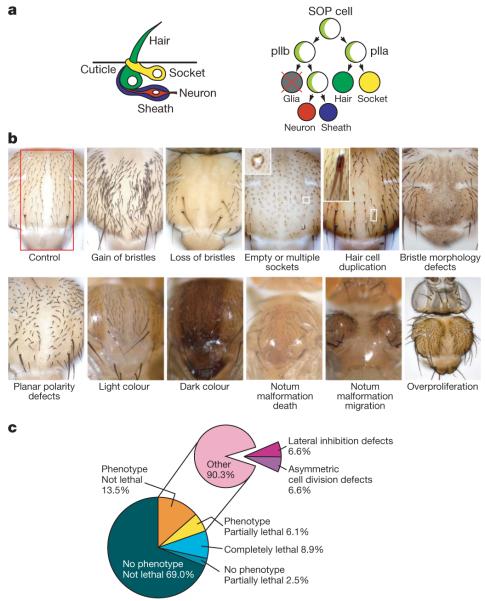
Figure 1. Phenotypic categories and screen results.
a, Schematic view of external sensory organ morphology and lineage (Numb and Neuralized, light green). b, Typical examples of phenotypic categories. The pannier-GAL4 expression area is indicated (red) in the control panel. Examples are Delta (gain of bristles), O-fut1 (loss of bristles), numb (empty or multiple sockets), bazooka (hair cell duplication), CG31961 (bristle morphology defects), starry night (planar polarity defects), CG18095 (light colour), CG34331 (dark colour), CG5462 (notum malformation death), CG7904 (notum malformation migration) and mob as tumor suppressor (overproliferation). Original magnification, ×10 (except overproliferation, ×5). c, Relative frequency of phenotypes in the entire primary genome-wide screen (left) and among visible phenotypes (right).