Figure 2.
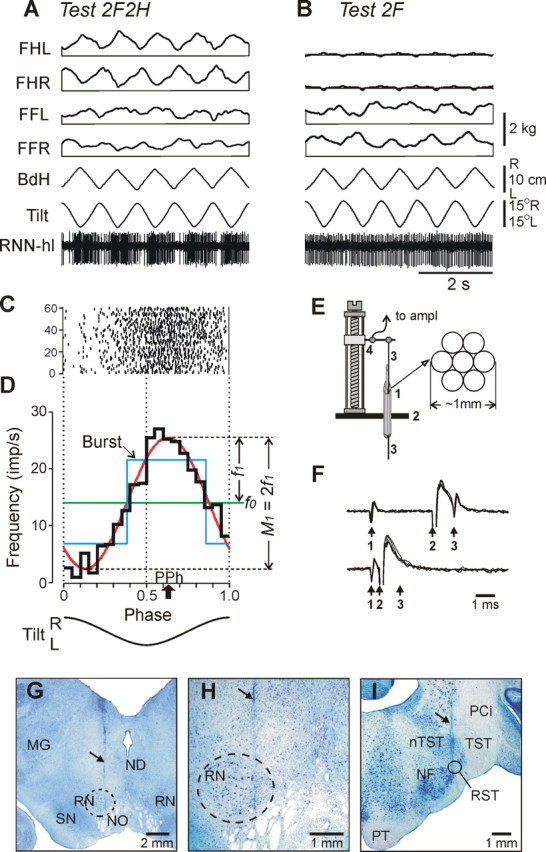
Representative example of postural and RNN responses (A–D), methods of RNN recording and identification (E, F), and histological verification (G–I). A, B, In tests 2F2H and 2F, the following traces are shown: RNN-hl—activity of a hindlimb-related RNN; Tilt—tilt of the platform; BdH—lateral displacement of the hind part of the body; FHL, FHR—contact forces under hindlimbs, left and right; FFL, FFR—contact forces under forelimbs, left and right. C, Raster of neuronal activity in 60 sequential cycles. D, Characteristics of neuronal activity: the histogram of spike activity in the tilt cycle (thick black line); first harmonic of Fourier image (red line) with its amplitude (f1) and the value of modulation (M1) indicated; mean frequency in the tilt cycle (f0, green line); preferred phase of the discharge (PPh, arrow). E, The method of inserting the microelectrode. A group of seven 28 gauge cannulas (1) are implanted through the opening in the scull (2) ∼10 mm above the red nucleus. The electrode (3) is manually inserted into one of the cannulas and soldered to an arm of a micromanipulator (4). F, Collision test determines whether RNN response is antidromic. Top trace, The RNN spontaneously discharges (arrow 1), and the rubrospinal tract is stimulated ∼3 ms later (arrow 2). The RNN responds with latency of ∼1 ms (arrow 3). Bottom trace, The RNN spontaneously discharges (arrow 1), and the rubrospinal tract is stimulated ∼0.5 ms later (arrow 2). RNN does not respond (arrow 3) because in 0.5 ms its spontaneous spike was still en route to the site of stimulation in the rubrospinal tract, and thus collision/nullification of spontaneous and evoked spikes occurred. G, H, Position of the microelectrode track within the left red nucleus (increased magnification in H). I, Position of the track of the stimulating electrode within the right rubrospinal tract. In G–I, the tracks are indicated by arrows. MG, Medial geniculate body; ND, nucleus Darkschewitsch; NF, nucleus of facial nerve; NO, n. oculomotorius; nTST, nucleus of tractus spinalis nervi trigemini; PCi, pedunculus cerebellaris inferior; PT, pyramidal tract; RST, rubrospinal tract; SN, substantia nigra; TST, tractus spinalis nervi trigemini.
