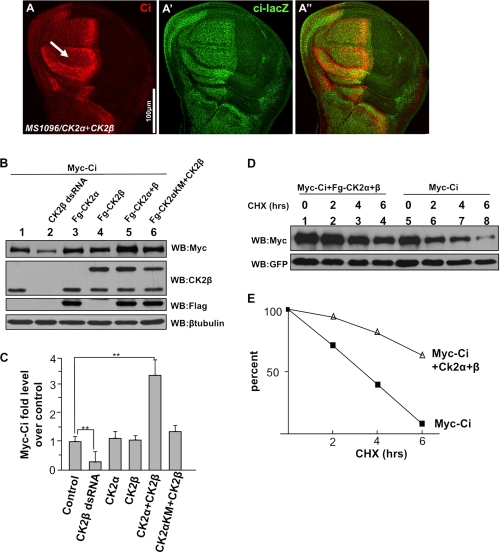
FIGURE 5.
CK2 up-regulates Ci by blocking Ci degradation. A–A″, wing disc coexpressing FLAG-CK2α and FLAG-CK2β immunostained for Ci and Ci-lacZ. Of note, Ci, but not Ci-lacZ, was elevated by CK2. B, CK2 kinase activity required for Ci stabilization. Myc-Ci was transfected into S2 cells with either the indicated CK2 constructs or the treatment of CK2β dsRNA. Cell extracts were subjected to direct Western blotting (WB) with anti-Myc antibody to detect the levels of Myc-Ci, with anti-CK2β antibody to detect the exogenous CK2β expression and the endogenous CK2β level that indicates the efficiency of CK2β RNAi, with anti-FLAG antibody to detect the FLAG-tagged CK2α, with anti-β-tubulin antibody to detect β-tubulin that served as loading control. C, quantification of Myc-Ci relative levels. The level of Ci from cells transfecting Myc-Ci alone was set as 1. **, p < 0.01 (Student's t test). D, S2 cells cotransfected with Myc-Ci and GFP, or with Myc-Ci, GFP, and FLAG-CK2α plus FLAG-CK2β, followed by treatment with cycloheximide for the indicated times. GFP expression served as transfection control. E, quantification of Ci levels from Western blot analysis performed in D. CHX, cycloheximide.