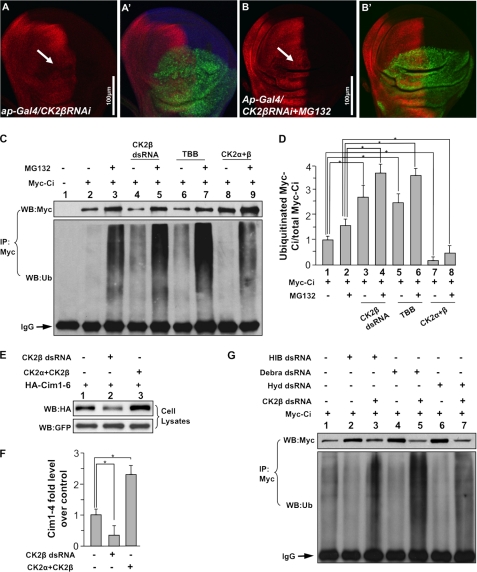
FIGURE 6.
CK2 down-regulates Ci ubiquitination and prevents the proteasome-mediated Ci degradation. A–B′, wing discs expressing UAS-CK2βRNAi by ap-Gal4 were treated with or without MG132 and immunostained for Ci. The treatment of MG132 restored Ci that was down-regulated by CK2β RNAi. GFP marks the RNAi cells. C, CK2 down-regulates Ci ubiquitination. S2 cells were transfected with Myc-Ci and incubated with CK2β dsRNA, or TBB, or cotransfected with FLAG-CK2α and FLAG-CK2β, followed by the treatment with or without MG132. Cell extracts were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-Myc antibody and blotted (WB) with anti-Myc antibody to determine the levels of Ci, or blotted with anti-ubiquitin antibody to examine the Ci-bound ubiquitin. IgG served as loading control. D, quantification analysis shows the ratio of ubiquitinated Ci to total Ci in C. Myc-Ci in lane 1 of C was set as 1. *, p < 0.05 (Student's t test). E, Cim1–6, with HIB-interacting sites mutated, is still regulated by CK2. S2 cells were cotransfected with HA-Cim1–6 and GFP, with either CK2α+CK2β or CK2β dsRNA treatment. Cell lysates were subjected to direct Western blotting with anti-HA antibody. F, quantification of HA-Cim1–6 relative levels from E is shown. The level of Cim1–6 from cells transfecting HA-Cim1–6 alone was set as 1. *, p < 0.05 (Student's t test). G, knockdown of the known E3s does not affect Ci ubiquitination that is induced by CK2 inactivation. S2 cells were transfected with Myc-Ci and treated with HIB dsRNA, Debra dsRNA, or Hyd dsRNA, with or without CK2β dsRNA. Cell extracts were immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc antibody and blotted with anti-Myc or anti-ubiquitin antibodies. IgG served as loading control.