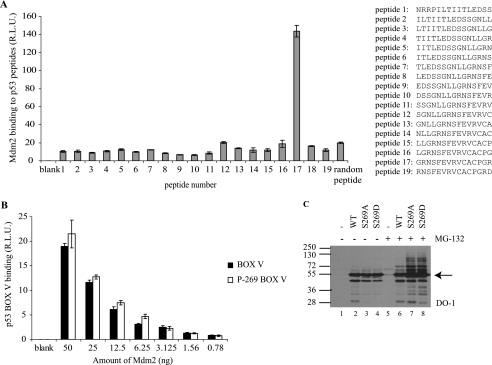
FIGURE 1.
Mutation of p53 at codon 269 increases p53 ubiquitination. A, mapping the region of p53 DNA-binding domain bound by MDM2. MDM2 binding to p53 peptides was determined by ELISA. Streptavidin-coated plates were coated with biotinylated peptides and incubated with MDM2, and the amount of MDM2 captured was determined using monoclonal 2A10 followed by chemiluminescence. The data are plotted as MDM2 binding (relative light units) as a function of MDM2 levels. B, effects of serine 269 phosphorylation on MDM2 binding to its p53-DNA-binding domain docking site. MDM2 binding to wild type and Ser269-phosphorylated p53 BOX-V domain peptide (LGRNSFEVR) was examined by ELISA as in A. C, mutation of p53 at codon 269 increases p53 ubiquitination. pcDNA expression vectors encoding p53, p53S269A, or p53S269D were transfected into H1299 cells (without or with 10 μm MG-132 treatment for 4 h prior to harvesting). Lysates (10 μg) were immunoblotted with DO-1 to detect total p53 and total ubiquitin-like modification of p53. Arrow indicates p53. R.L.U., relative light units. Error bars, S.D.