Table 2.
Effects of viral gene manipulation on the coupling between 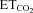 and discharge properties of inspiratory HMNs
and discharge properties of inspiratory HMNs
| Experimental conditions | n | SmFR (sp s−1%−1) | SSB (sp burst−1%−1) | SBR (bursts min−1%−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intact (control) | 44 | 9.2 ± 0.9 | 4.6 ± 0.4 | 5.6 ± 0.8 |
| 7 days post-crushing | 44 | 3.5 ± 0.4* | 1.5 ± 0.2* | 4.1 ± 0.6 |
| AVV-eGFP | 25 | 10.1 ± 0.8 | 6.2 ± 0.6 | 4.1 ± 1.2 |
| AVV-eGFP/AVV-nNOS | 16 | 3.5 ± 0.5*# | 1.7 ± 0.4*# | 4.2 ± 2.3 |
| AVV-eGFP/AVV-nNOS+L-NAME | 16 | 8.2 ± 2.0§ | 5.0 ± 1.1§ | 3.1 ± 1.1 |
| AVV-eGFP/AVV-nNOS+7-NI | 10 | 10.7 ± 1.1§ | 6.4 ± 1.3§ | 4.1 ± 0.4 |
| AVV-eGFP/AVV-nNOS+ODQ | 12 | 13.4 ± 2.5§ | 6.4 ± 1.1§ | 6.2 ± 1.5 |
| LVV-miR-shRNA/nNOS/AVV-nNOS | 16 | 10.7 ± 1.0§ | 6.3 ± 0.5§ | 3.5 ± 1.6 |
| LVV-miR-shRNA/nNOS/Crush | 11 | 7.3 ± 0.9 | 3.7 ± 0.4 | 5.7 ± 0.9 |
| LVV-miR-shRNA/nNOS/Crush +Dox | 9 | 4.2 ± 1.2* | 1.8 ± 0.5* | 6.3 ± 3.2 |
Sensitivity (S) or gain parameters characterizing motoneuron activity were measured in response to 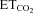 changes from 3–3.5% to 5.5–6.0%. n represents the number of motoneurons included in the study. Data values are expressed as means ±s.e.m. At least 3 animals were used per experimental condition. Significant differences relative to intact/control
changes from 3–3.5% to 5.5–6.0%. n represents the number of motoneurons included in the study. Data values are expressed as means ±s.e.m. At least 3 animals were used per experimental condition. Significant differences relative to intact/control
AVV-eGFP-
or AVV-eGFP/AVV-nNOS-injected
groups (P < 0.05; one-way ANOVA; post hoc Tukey's test).
