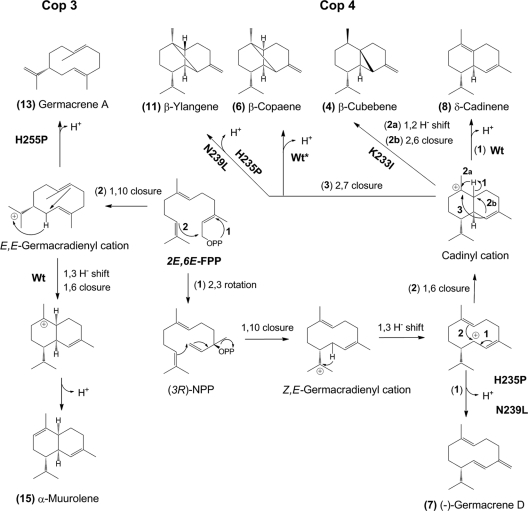
FIG. 4.
Proposed cyclization pathways of wild-type and H-α1-loop mutants of Cop3 (left side) and Cop4 (right side). Cyclization of E,E-FPP by Cop4 involves an ionization/isomerization step to yield (3R)-nerolidyl diphosphate [(3R)-NPP] (22) which, after ionization and 1,10-ring closure, gives a Z,E-germacradienyl cation that is further rearranged to the different cyclization products of Cop4 wild type and loop mutants. The major cyclization products of Cop3 and its loop mutants are derived from a E,E-germacradienyl cation formed after ionization and 1,10 cyclization of E,E-FPP (2, 3). Shown are cyclization pathways to major products of Cop3 and Cop4 wild type and loop mutants that significantly impact product outcomes of the two enzymes. Compound numbers correspond to sesquiterpenes in the product profiles shown in Fig. 2 to 4. Numbered reaction arrows indicate different branch points in the cyclization reaction.