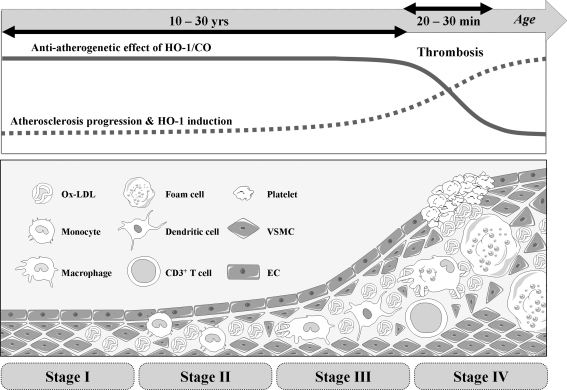
FIG. 8.
Role of HO-1/CO in atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis initiates from the oxidation of accumulated lipoprotein in subendothelial layer of blood vessel. Oxidized LDL induces production of inflammatory cytokines and metalloproteinases, which can breakdown extracellular matrix network. As disease progresses, inflammatory cells are infiltrated and especially monocytes are differentiated to foam cells. SMCs in media are proliferated and migrated to make intima. As the atherosclerotic lesion progress, ECs and SMCs gradually express HO-1, which is mainly induced by oxidized LDL and hypoxia, whereas cells at early stage barely express HO-1. Delivering HO-1/CO to the atherosclerotic lesion helps stabilizing the lesion by enhancing EPC recruitment, EC proliferation/survival, and inhibition of VSMC growth/migration. However, delivering HO-1/CO in advanced lesions does not show much protective effects. LDL, low-density lipoprotein.