Figure 1.
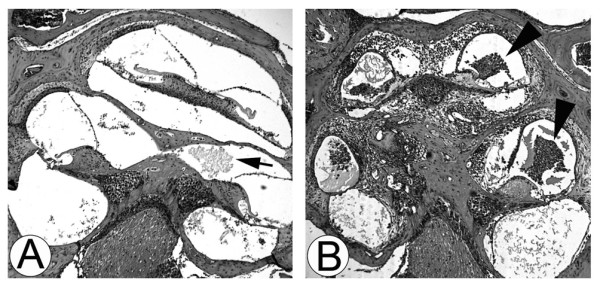
Inner ear inflammation secondary to NTHI-induced middle ear infection. Live NTHI was inoculated into the murine middle ear through the tympanic membrane and temporal bones were harvested at 7 days after bacterial inoculation. H & E staining shows that middle ear infection results in serous labyrinthitis (A) and purulent labyrinthitis (B). Note accumulation of serous substances with hemorrhage (arrow) and massive infiltration of inflammatory cells (arrowhead) in the cochlear spaces. Original magnification: ×50.
