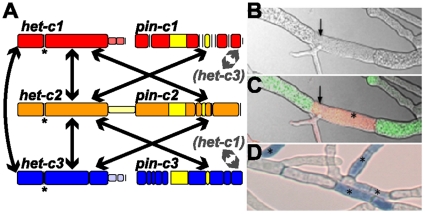
Figure 1. Diagram of the three het-c/pin-c haplotypes in N. crassa and death of fusion cells as a consequence of heterokaryon incompatibility.
A). Cartoon diagram of het-c1/pin-c1, het-c2/pin-c2 and het-c3/pin-c3 haplotypes. Nonself recognition is mediated by genetic interactions between het-c and pin-c from alternate haplotypes (het-c1-pin-c2, het-c1-pin-c3, het-c2-pin-c1, het-c2-pin-c3, het-c3-pin-c1 or het-c3-pin-c2; arrows). Allelic interactions between alternate het-c alleles (het-c1-het-c2, het-c1-het-c3 or het-c2-het-c3) is required for a robust HI response [26], [38]; arrows. The allelic specificity domain of het-c is indicated by an asterisk ‘*’ [38]. Thinner bars indicate intergenic sequence and indels are represented by open spaces. The HET domain of pin-c is shown in yellow. (B–D) Confocal micrographs showing hyphal fusion and heterokaryon formation between a het-c1/pin-c1 strain bearing cytoplasmic GFP and a het-c2/pin-c2 strain carrying a nuclear histone HI dsRED marker (isolates are otherwise isogenic). (B) Differential interference contrast (DIC) micrographs. Arrow indicates cell fusion point. (C) merged image of incompatible fusion [7]. Arrow indicates cell fusion point and asterisk indicates compartmentalized hyphal segment. (D) Hyphae stained with the vital dye Evan's blue [89]. Asterisks show compartmentalized dead hyphal segments.