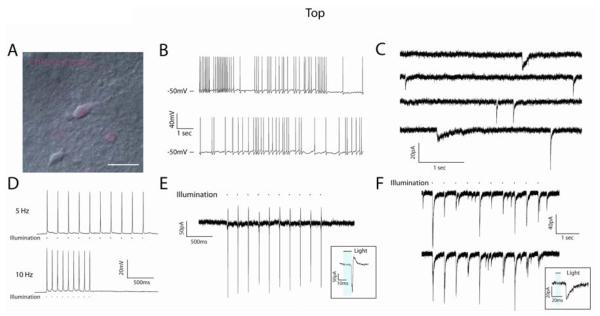
Figure 3.
ChR2-induced currents in hESC-derived neurons in acute slice preparations. (A) DIC/fluorescent image of a hESC-derived neuron recorded in an acute slice preparation from a 5 month-old SCID mouse. (B) Current-clamp traces demonstrating the presence of spontaneous AP generation. (C) Voltage-clamp recordings demonstrating the presence of spontaneous PSCs with different temporal kinetics, indicative of both excitatory and inhibitory synapses. (D) Representative current-clamp traces of ChR2-induced spiking at 5Hz (upper) and 10Hz (lower) frequencies in response to 470nm light stimulation. (E) 5Hz train of APs generated in response to light stimulus and recorded in the on-cell configuration, demonstrating the ability of hESC-derived neurons to generate mature spikes (inset) without experimental alteration of resting membrane potential. (F) Representative traces from ChR2− cells that showed PSCs in response to light stimulation of the slice. Inset illustrates the temporal delay between light stimulus (blue bar) and PSC onset. Scale bar represents 20μm.