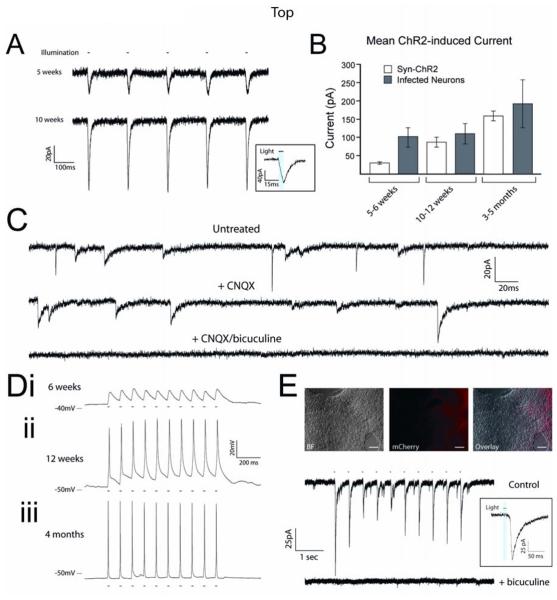
Figure 5.
Synapsin-ChR2-mCherry cell line exhibits a full complement of optically-induced currents. (A) Representative traces of ChR2 currents from Syn-ChR2 neurons at 5 and 10 weeks; inset shows light-current relationship. (B) Pooled data demonstrates that the ChR2-mediated currents in the cell line increased during differentiation in response to 10ms light stimuli, and displayed less variation compared with hESC-derived neurons that were infected upon differentiation. (C) Representative voltage-clamp traces from Syn-ChR2-derived neurons after 10 weeks of differentiation illustrate the presence of ePSCs and iPSCs. ePSCs were specifically blocked by application of CNQX (50μM) and iPSCs were blocked by bicuculine (20μM). (D) Representative current-clamp traces from Syn-ChR2-mCherry neurons in response to 10Hz stimulations at 6 weeks (i), 12 weeks (ii) and 4 months (iii) of differentiation. (E) Paired Hoffman contrast and fluorescent images of co-cultures of wild-type hESC-derived neurons and Syn-ChR2-mCherry neurons. Representative voltage-clamp recording of a ChR2− cell that generated post-synaptic currents in response to 470nm light stimuli (upper trace), and could be blocked with bicuculine (lower trace). Inset shows light-current relationship. Error bars represent SEM. Scale bars indicate 100μm.