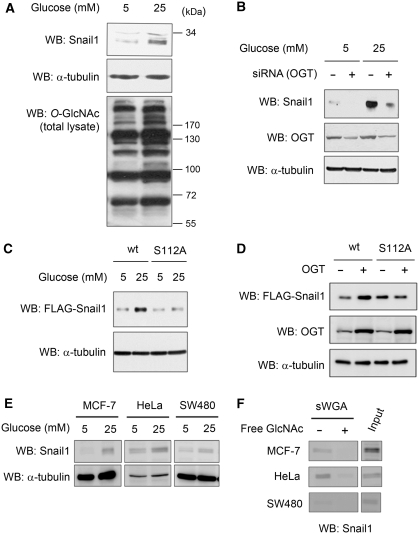
Figure 4.
Hyperglycaemic condition increases Snail1 in an OGT-dependent manner. (A) Western blot analysis for endogenous Snail1 and O-GlcNAc from A549 cells under normoglycaemic (5 mM) and hyperglycaemic (25 mM) conditions. α-tubulin is shown as the loading control. (B) siRNA-mediated knock-down of OGT and western blot analysis for endogenous Snail1 or OGT from A549 cells under normo- and hyperglycaemic conditions. α-tubulin was included as a loading control. (C) Western blot analysis of wt or S112A mutant Snail1 from HEK293 cells under normo- and hyperglycaemic conditions. α-tubulin is shown as the loading control. (D) Western blot analysis of wt or S112A mutant Snail1 in HEK293 cells overexpressing OGT. α-tubulin is shown as the loading control. (E) Western blot analysis for endogenous Snail1 from MCF-7, HeLa, and SW480 cells under normoglycaemic (5 mM) and hyperglycaemic (25 mM) conditions. α-tubulin is shown as the loading control. (F) MCF-7, HeLa, and SW480 cells were grown under hyperglycaemic condition (25 mM) and their cell lysates were subjected to sWGA-lectin-affinity purification and the precipitates analysed with western blot for endogenous Snail1. The inhibitory monosaccharide GlcNAc (20 mM) was added during sWGA-lectin-affinity purification.