Figure 7.
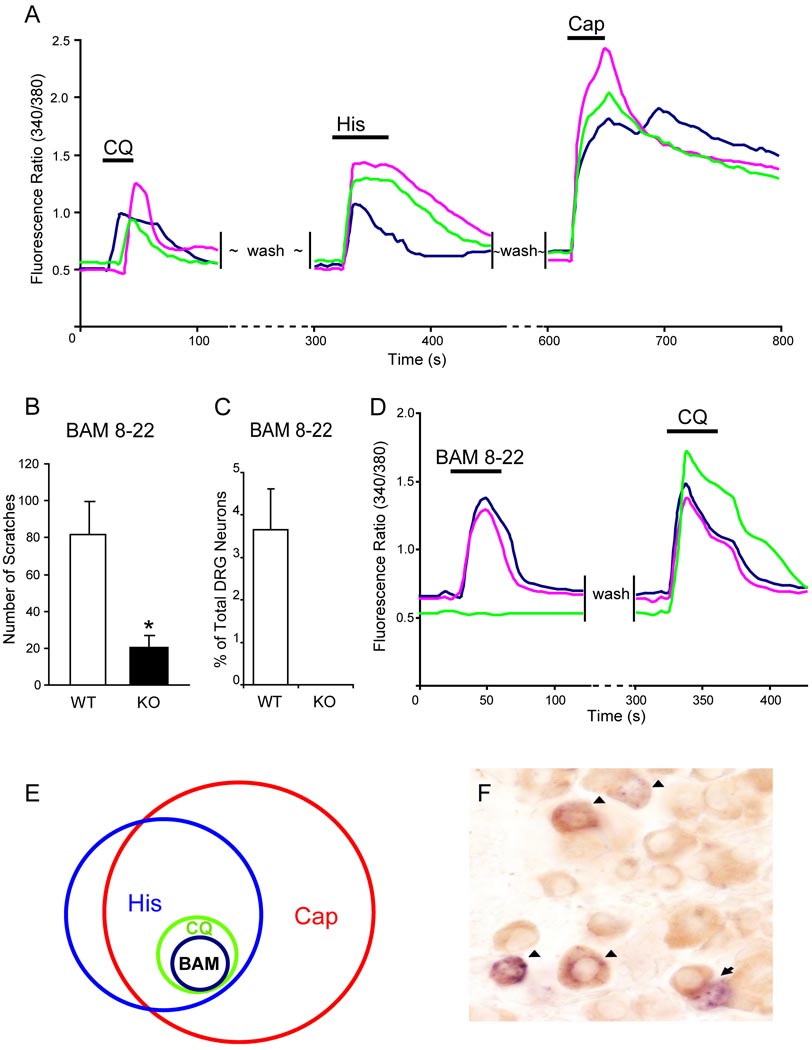
CQ-responsiveness defines a specific subpopulation of DRG neurons. (A) CQ-responsive neurons represented a small population of DRG neurons that also responded to histamine (50 µM) and capsaicin (1 µM) with increased [Ca2+]i monitored by calcium imaging. (B) The total scratching bouts during the first 30 min after BAM8-22 intradermal injection (50 µI of 1 mM). WT mice exhibited significantly stronger scratching responses after injection than Mrgpr-clusterΔ−/− littermates did (n=8 per genotype; * p<0.05). (C) As determined by calcium imaging, 3.6% of WT DRG neurons responded to BAM8-22 (2 µM) with increased [Ca2+]i and all of them are also CQ-sensitive (D), whereas Mrgpr-clusterΔ−/− DRG neurons failed to respond to the drug (n=3 per genotype) (C). (E) The Venn diagram illustrates the relationships of histamine- (His), capsaicin- (Cap), chloroquine- (CQ), and BAM8-22- (BAM) responsive neurons in adult DRG. The sizes of the circles are proportional to the sizes of the cell populations. (F) WT adult DRG sections were doubly stained by in situ hybridization for MrgprA3 (blue) and immunostaining using anti-GRP antibody (brown). Most MrgprA3+ cells (51 out of 55) express GRP. Arrowheads indicate MrgprA3/GRP co-expressing neurons. Arrows indicate MrgprA3+/GRP− cells.