Figure 3.
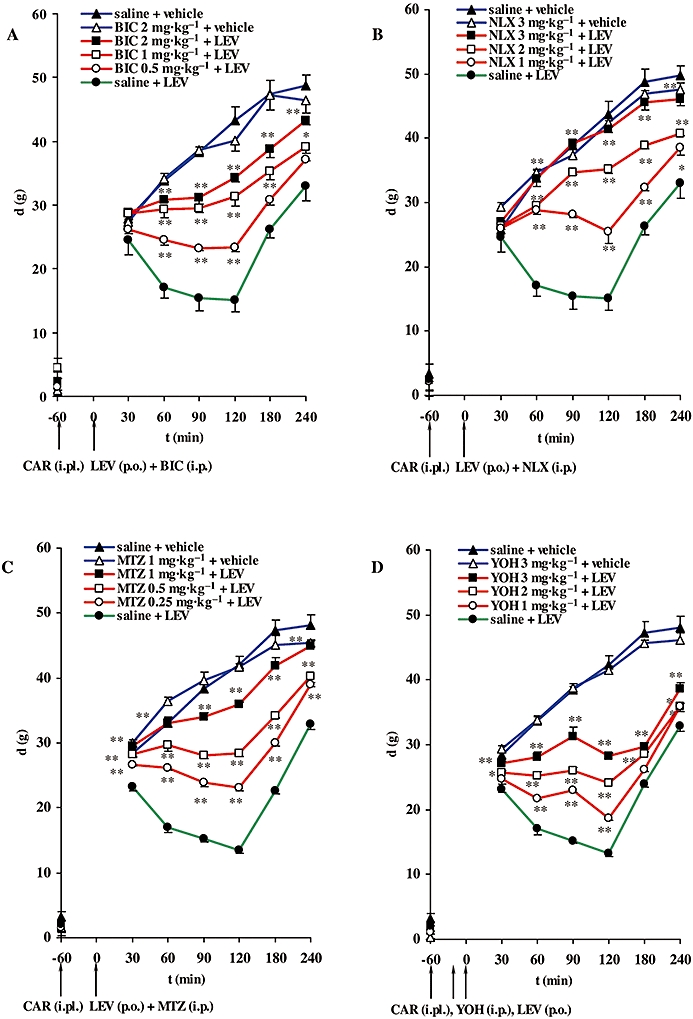
Time course of the inhibitory effects of bicuculline (BIC) (A), naloxone (NLX) (B), methysergide (MTZ) (C) and yohimbine (YOH) (D) on the antihyperalgesic effect of levetiracetam (LEV), expressed as the difference in pressure g (d) applied to non-inflamed and inflamed (CAR-injected) rat hind paws. Pretreatment d (plotted on the vertical axis) was obtained before induction of inflammation. BIC (i.p.) (A), NLX (i.p.) (B), MTZ (i.p.) (C) were injected immediately prior to LEV administration (p.o.) and 60 min after injection of CAR; only YOH (i.p.) (D) was injected 15 min before LEV and 45 min after CAR (denoted by arrows). Each point represents the mean ± SEM of paw pressure differences (d) of 6–8 animals. Statistical significance (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; one-way anova with repeated measures followed by Bonferroni test) was determined by comparison of the curves obtained in the presence of the receptor antagonists with the curve for saline + LEV. i.pl., intraplantar.
