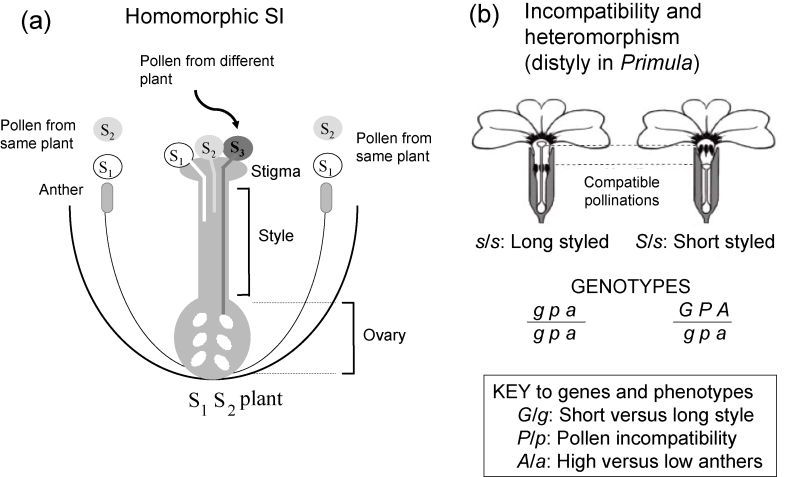
Figure 1. Flower parts and S genotypes.
(a) Homomorphic self-incompatibility (SI). Gametophytic control of pollen incompatibility types is shown; the haploid pollen grains express the allele they carry. This system is known in Solanaceae, Papaveraceae, Rosaceae, and Antirrhinum species (in an unrelated angiosperm family, Plantaginaceae). In other families, pollen specificities are controlled by the genotype of the diploid anther tissue (sporophytic system). This is known in Brassicaceae and in Ipomoea, in the family Convolvulaceae (e.g., [32]). (b) Heteromorphic SI. Long- and short-styled primrose flowers (showing the pollinations that are compatible) from [29-31] and the three genes hypothesised to control style length, pollen incompatibility type, and anther position.