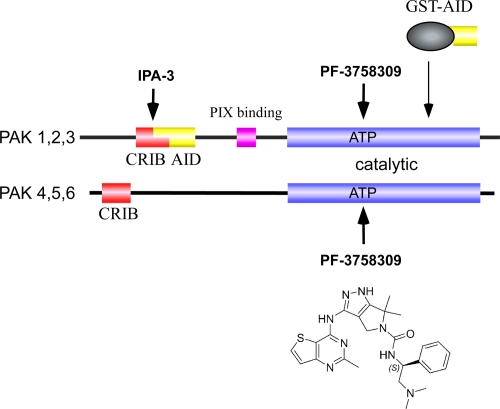
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the regions targeted by various p21-activated kinase (PAK) inhibitors.
Both group I and group II PAKs contain related catalytic and Cdc42/Rac interaction and binding (CRIB) domains. PAK1, PAK2, and PAK3 are inhibited in trans via an auto-inhibitory domain (AID), which when expressed as a glutathione S-transferase (GST) fusion protein can effectively inhibit the kinase [16]. The PAK1-, PAK2-, and PAK3-binding partner PIX (PAK-interacting exchange factor) interacts via a highly unusual SH3-interacting region [3]. The small-molecule inhibitor IPA-3 (p21-activated kinase inhibitor 3) is a symmetric dimer joined by a disulphide bond [19] which targets the CRIB region. The structure of PF-3758309 is shown for reference; PF-3758309 binds the ATP-binding pocket of PAKs as revealed by the X-ray structure of the PAK4-PF-3758309 complex [21].