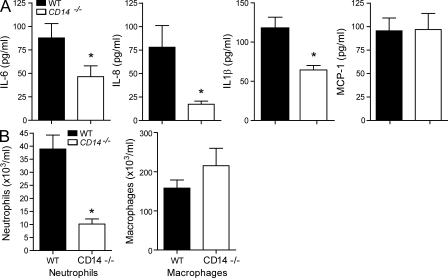
Figure 4.
CD14 is important for the proinflammatory response to CpG-DNA in vivo. WT or CD14−/− mice were i.p. injected with 8 nmol CpG-DNA. After 4 h, mice were sacrificed. (A) The levels of the proinflammatory cytokines IL-6, KC (IL-8), IL-1β, and MCP-1 in peritoneal lavage were analyzed by ELISA. (B) Peritoneal lavage was taken, and total cells, neutrophils, and macrophages were counted. Differences in cytokine values of WT and CD14−/− stimulation pairs were tested for significance using the one-way analysis of variance and Tukey’s post test. Significant alterations in pattern are marked with an asterisk (*, P < 0.05 vs. WT mice; Mann–Whitney T test). In A, P = 0.0434, P = 0.0005, and P = 0.0029 for IL-6, IL-8, and IL-1β, respectively. In B, P = 0.0002 for neutrophils. Data are presented as mean ± SD and are representative of two independent experiments, each performed with eight mice/group.