Figure 1. AurA Phosphorylates the Par Complex to Activate aPKC.
(A) Lgl is underphosphorylated in aurA mutants. Larval brain extracts of the indicated genotypes were analyzed.
(B) AurA induces the phosphorylation of Lgl by activation of aPKC. Immunoprecipitate (IP) from aurA37/Ac-3 brains was incubated with ATP and recombinant AurA as indicated.
(C) ClustalW alignment of the AurA phosphorylation site (red) in Par-6 orthologs. Residues identical or similar to the Drosophila protein are colored magenta and blue, respectively. The bottom line shows the AurA consensus (Ferrari et al., 2005); 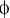 denotes any hydrophobic residue.
denotes any hydrophobic residue.
(D) Constructs used in the kinase assay.
(E) AurA phosphorylates Par-6 on Ser34 in vitro. Recombinant proteins were incubated with [32P]ATP and recombinant AurA as indicated. The gel was Coomassie-stained (CBB), followed by autoradiography (32P). The arrowhead indicates autophosphorylated AurA. Autoradiographs were quantified by summing the signal of the full-length bands and normalizing for the signal of Par-6WT (set to 1). Averages and standard deviations are shown (n = 4).
(F) AurA phosphorylates Par-6 on Ser34 in vivo. Phosphospecific antibodies directed against Ser34 were used to immunoprecipitate p-Par-6 from brains of the indicated genotypes. A second round (#2) of immunoprecipitation from the supernatant confirms the depletion of p-Par-6. To avoid the overlapping IgG signal and to control for the specificity of the antibodies, extracts from wild-type animals and from par-6Δ226 mutants complemented by a genomic rescue construct expressing Par-6-GFP (par-6GFP) were used.