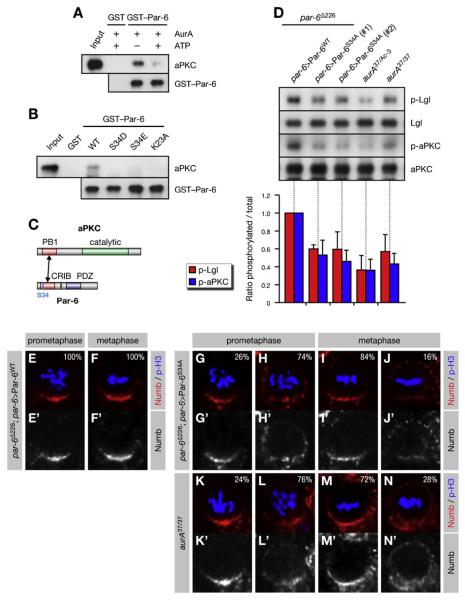
Figure 2. Phosphorylation of Par-6 on Ser34 Regulates aPKC Activity and Numb Localization.
(A–C) Phosphorylation of Par-6 on Ser34 regulates the interaction of Par-6 with aPKC. Recombinant proteins were used to precipitate aPKC from larval brains. (A) The baits were preincubated with recombinant AurA and ATP as indicated. (B) Phosphomimetic forms of Par-6 (S34D/E) and a control mutant (K23A) defective for binding to aPKC (Noda et al., 2003) were used in the pull-down assays. (C) Par-6 interacts with aPKC through dimerization of the PB1 domains.
(D) Phosphorylation on Ser34 is required for full activity of aPKC toward Lgl. Brain extracts from par-6 mutants complemented by genomic rescue constructs expressing either Par-6WT or Par-6S34A were analyzed; aurA mutants were included as controls. (#1) and (#2) refer to independent insertions of the rescue construct. Western blots were quantified and normalized for Par-6WT (set to 1). Averages and standard deviations are shown (n = 3). Differences in p-aPKC and p-Lgl levels between aurA37/37 and par-6S34A brains are insignificant (p > 0.45 and p > 0.81, respectively).
(E–N) Phosphorylation on Ser34 is required for timely Numb localization. Larval neuroblasts of the indicated genotypes were stained for p-H3 to label DNA in mitotic cells and for Numb. Apical is up. Percentages shown for prometaphase cells include late prophase cells.