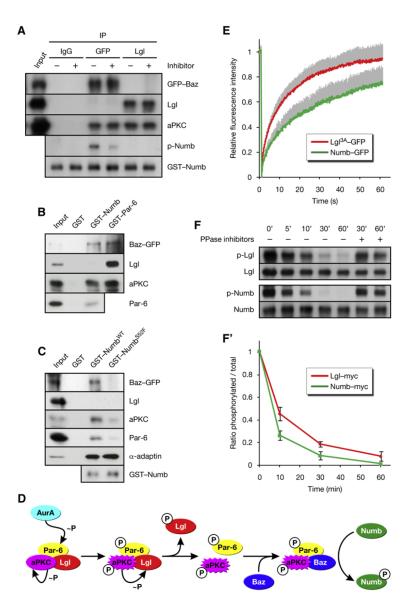
Figure 6. Baz Changes the Substrate Specificity of aPKC.
(A) Baz and Lgl assemble into distinct Par complexes with differential activity toward Numb. Baz and Lgl complexes were isolated from bazCC01941 embryos expressing Baz-GFP by immunoprecipitation (IP) of GFP and Lgl, respectively. The immunoprecipitates were incubated with recombinant Numb, ATP, and aPKC inhibitor where indicated.
(B) Numb is in the Baz complex, but not in the Lgl complex. Recombinant proteins were used in pull-down assays from embryos expressing Baz-GFP.
(C) NumbS52F is not in the Baz complex. Recombinant proteins were used in pull-down assays from larval brains expressing Baz-GFP.
(D) Proposed mechanism whereby the activation of AurA leads to the phosphorylation of Numb.
(E) Lgl has higher cortical mobility than Numb. Lgl3A-GFP and Numb-GFP were photobleached on the anterior cortex of pupal SOP cells in metaphase (see Figures S6B and S6C). and the recovery of fluorescence was recorded. The values were normalized to prebleach intensity after correction for background variation and fluorescence loss. Averages are plotted, and standard deviations for the individual time points are shown as gray bars (n = 33 for Lgl3A-GFP; n = 26 for Numb-GFP).
(F) Numb is dephosphorylated more rapidly than Lgl. myctagged Numb and Lgl were immunoprecipitated from embryos, in vitro phosphorylated by PKCz, and subjected to dephosphorylation by brain extract for the indicated durations. Addition of phosphatase inhibitors suppressed the decay of phosphospecific signal. (F’) Quantification of (F). Averages are plotted, and standard deviations for the individual time points are shown (n = 2).