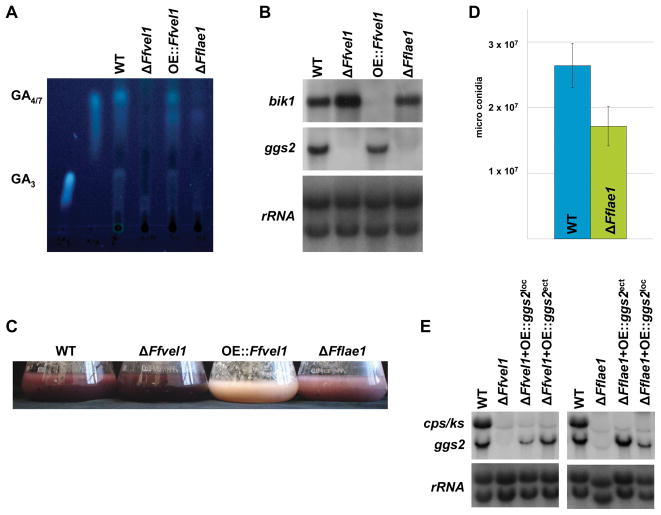
Figure 8. Analysis of the Fflae1 knock-out strains compared to the F. fujikuroi wild type IMI58289 in regard to secondary metabolism and conidiation.
A Thin layer chromatogram of the F. fujikuroi wild-type strain IMI58289, the Ffvel1 and Fflae1 knock-out strains as well as the overexpression strain OE::Ffvel1 grown in 10 % ICI cultures for 7 days. GA4/7 and GA3 were used as standards (for details see Experimental procedures).
B Expression of bik1 and ggs2 in the wild type, the Ffvel1 and Fflae1 knock-out strains as well as the OE::Ffvel1 overexpression mutant. The strains were grown for 3 days in 10 % ICI medium. 28S and 18S rRNA was visualized by EtBr staining as control.
C Photographs of the F. fujikuroi wild-type strain IMI58289, the Ffvel1 and Fflae1 knockout strains as well as the overexpression strain OE::Ffvel1 grown in 10 % ICI cultures for 3 days.
D Spores produced by the F. fujikuroi wild-type strain IMI58289 and the Fflae1 knock-out strain grown for 10 days on V8 solidified media under constant light conditions. Experiment was carried out on triplicate; bars show standard deviations.
E Expression of ggs2 and cps/ks in the wild type, the Ffvel1 and Fflae1 knock-out strains as well as in strains expressing ggs2 in the GA gene locus (ΔFfvel1+OE::ggs2loc and ΔFflae1+OE::ggs2loc) or ectopically (ΔFfvel1+OE::ggs2ect and ΔFflae1+OE::ggs2ect), respectively. The strains were grown for 3 days in 10 % ICI medium. 28S and 18S rRNA was visualized by EtBr staining as control.