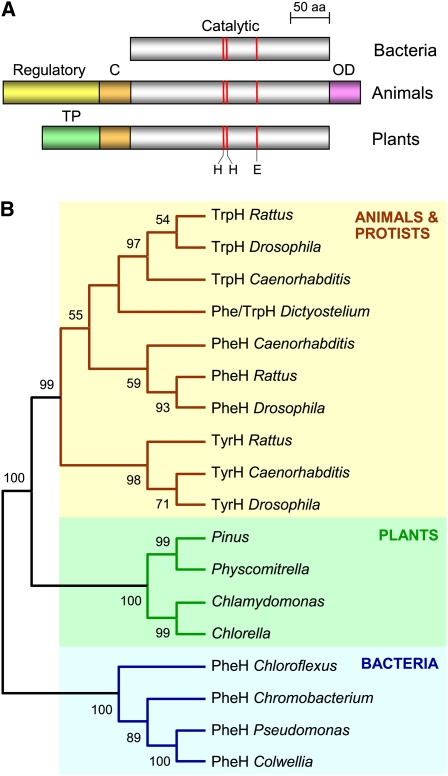
Figure 2.
Overall Domain Structures and Phylogenetic Relationships of Aromatic AAH Family Proteins.
(A) Comparison of the domain structures of bacterial, animal, and plant AAH proteins. Note the common catalytic domain and its conserved extension (C) in animal and plant AAHs, the unique regulatory and oligomerization (OD) domains in animal AAHs, and the putative targeting peptide (TP) in plant AAHs. Red lines mark the sites of iron-liganding His and Glu residues.
(B) Unrooted neighbor-joining tree for AAH proteins. Bootstrap values (1000 replicates) are indicated for nodes with >50% support. Only the tree topology is shown, so that branch lengths are not proportional to estimated numbers of amino acid substitutions. Enzymatic activities (based on published biochemical and/or genetic evidence): PheH, phenylalanine hydroxylase; TyrH, tyrosine hydroxylase; TrpH, tryptophan hydroxylase. Full organism names: Caenorhabditis elegans, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, Chlorella sp NC64A, Chloroflexus aurantiacus, Chromobacterium violaceum, Colwellia psychrerythraea, Dictyostelium discoideum, Drosophila melanogaster, Physcomitrella patens, Pinus taeda, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Rattus rattus.