Figure 3.
Evidence that Plant AAH Proteins Have Tetrahydropterin-Dependent Phe Hydroxylase Activity.
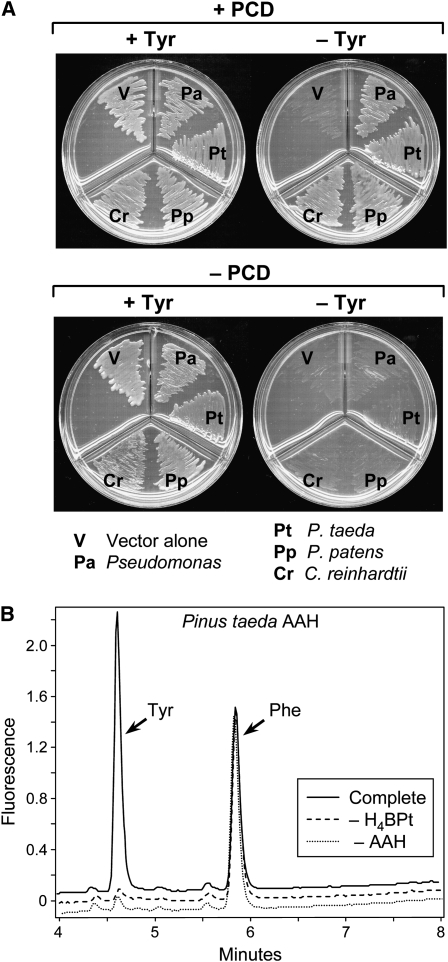
(A) Detection of Phe hydroxylase activity by functional complementation. An E. coli Tyr auxotroph was transformed with pBluescript alone (– PCD) or containing the P. aeruginosa gene encoding PCD (+ PCD), plus the pSU18 vector alone or containing the P. aeruginosa Phe hydroxylase gene or a plant AAH cDNA (truncated to remove the putative targeting peptide). The doubly transformed cells were plated on minimal medium containing IPTG, plus or minus Tyr (+Tyr and −Tyr).
(B) Phe hydroxylase activity of recombinant P. taeda AAH. The complete reaction comprised 1 mM Phe, 0.2 mM H4BPt, 50 μM Fe(NH4)2(SO4)2, 10 mM DTT, 40 units of catalase, and extract (10 μg protein) from E. coli BL21-CodonPlus (DE3)-RIPL cells harboring pET28b containing P. taeda AAH cDNA. Controls were run without H4BPt (– H4BPt) or with extract from E. coli cells harboring pET28b alone (– AAH). Incubation was at 30°C for 15 min. Reactions were analyzed by fluorometric HPLC.