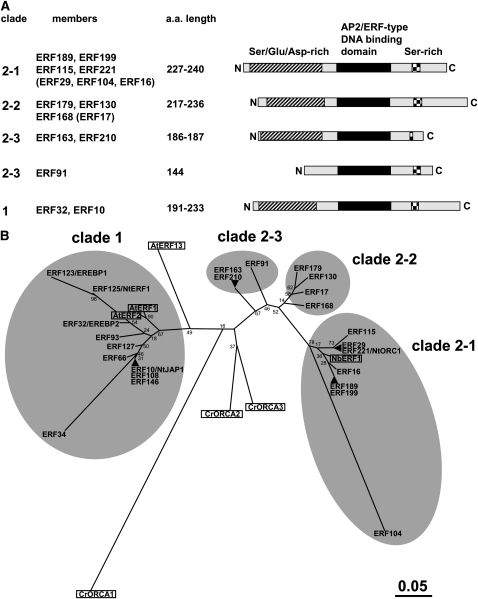
Figure 1.
Group IXa ERF Members in Tobacco.
(A) Structure of tobacco IXa ERFs. Diagrams show the positions of the conserved AP2/ERF DNA binding domain, a Ser/Asp/Glu-rich region, and a short Ser stretch in four clades (1, 2-1, 2-2, and 2-3). Available cDNA clones for ERF29, ERF104, ERF16, and ERF17 (shown in parentheses) do not contain full-length coding sequences. ERF91 is truncated at the N terminus. a.a., amino acid.
(B) Phylogenetic tree of tobacco IXa ERFs and other homologous proteins based on the alignment of their AP2/ERF domain sequences (available as Supplemental Data Set 1 online). The tree was generated using MEGA4 software (Tamura et al., 2007) with the neighbor-joining algorithm. Bootstrap values are indicated at branch nodes, and the scale bar indicates the number of amino acid substitutions per site. Two or three ERFs located at the same place (e.g., ERF189 and ERF199) indicate homologous tobacco ERF proteins whose AP2/ERF domains are identical in amino acid sequence. At ERF1 (At4g17500), At ERF2 (At5g47220), and At ERF13 (At2g44840) are from Arabidopsis, Cr ORCA1, Cr ORCA2, and Cr ORCA3 are from C. roseus, and Nb ERF1 is from N. benthamiana.