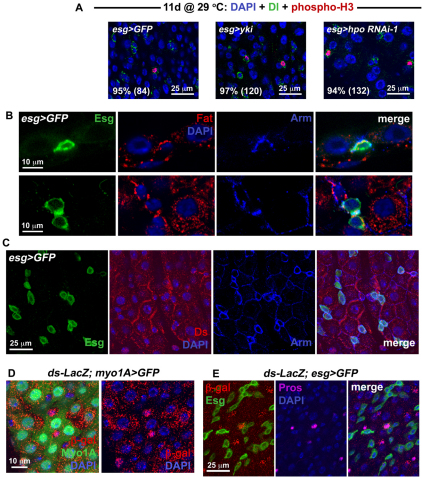
Fig. 3.
Hippo signaling occurs in different cell types within the midgut epithelium. (A) Confocal images show wild type (left panel is esg>GFP: w1118/+; esg-Gal4, UAS-GFP, Tub-Gal80TS/+), overexpression of yki (center panel is esg>yki: esg-Gal4, UAS-GFP, Tub-Gal80TS/+; UAS-yki/+) and RNAi against hpo (right panel is esg>hpo RNAi-1: esg-Gal4, UAS-GFP, Tub-Gal80TS/+; hpo RNAi-1/+) stained for Dl (green) and phosphorylated Histone 3 (red). Nearly all mitotic cells are also Dl(+), as revealed by quantification of percentages (number of phospho-H3 cells counted are in brackets). (B) Fat staining is located in the basal region of wild-type posterior gut epithelium. Top panels show confocal sections through the epithelial wall, with an ISC labeled for Esg (green) located basally. The outside of the gut is just below the ISC. A crescent of Fat protein, coincident with Armadillo (Arm) which marks the cell cortex, is located between the ISC and its neighboring EC cells. Lower panels show confocal sections taken through the basal region of the epithelium, where ISC/Eb cells are located. Fat staining is present around the cortex of Esg(+) cells. (C) Confocal images show that the Ds protein, also coincident with Arm, is located at the edges of wild-type ECs – in some cases where the ECs appose Esg(+) cells. (D) Confocal images of a Tub-Gal80TS/ds-LacZ; myo1A-Gal4, UAS-GFP/+ posterior midgut. ds-LacZ is expressed in the EC cells which are GFP-labeled using the NP1 Gal4 driver. (E) Confocal images of a ds-LacZ/+; esg-Gal4, UAS-GFP, Tub-Gal80TS/+ midgut. Strong ds-LacZ expression is also present in Pros(+) ee cells.