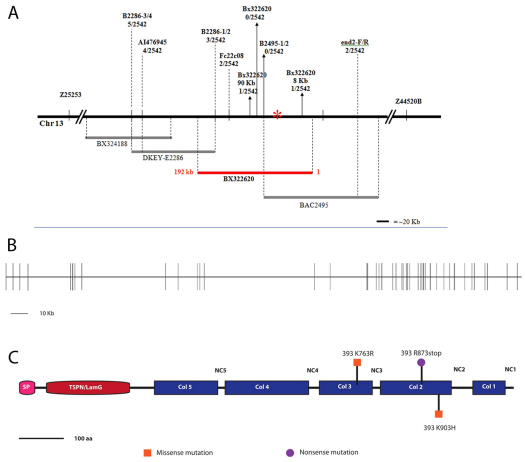
Fig. 1.
Positional cloning of the stumpy gene. (A) The stumpyb393 mutation was mapped to chromosome 13 (Chr 13) and further mapped to BAC BX322620. The solid black line represents the relevant genomic region on Chr 13; lines beneath indicate individual BACs that were mapped to this region with the stumpy BAC in red; primer names and number of recombinants are listed above the line. The asterisk denotes the location of the stumpy gene coincident with the location of ColXIX. (B) Intron-exon structure of the ColXIX gene. The gene consists of 50 exons and spans ∼300 kb. (C) ColXIX protein structure with stumpyb393 mutations indicated. ColXIX is composed of an N terminus head consisting of a signal peptide and a LamG/TSPN domain (red). The C-terminal tail has five collagenous domains (Col1-Col5) ranging from 72 amino acids to 186 amino acids in length interrupted by five non-collagenous domains (NC1-NC5) ranging from 18 amino acids to 158 amino acids in length.