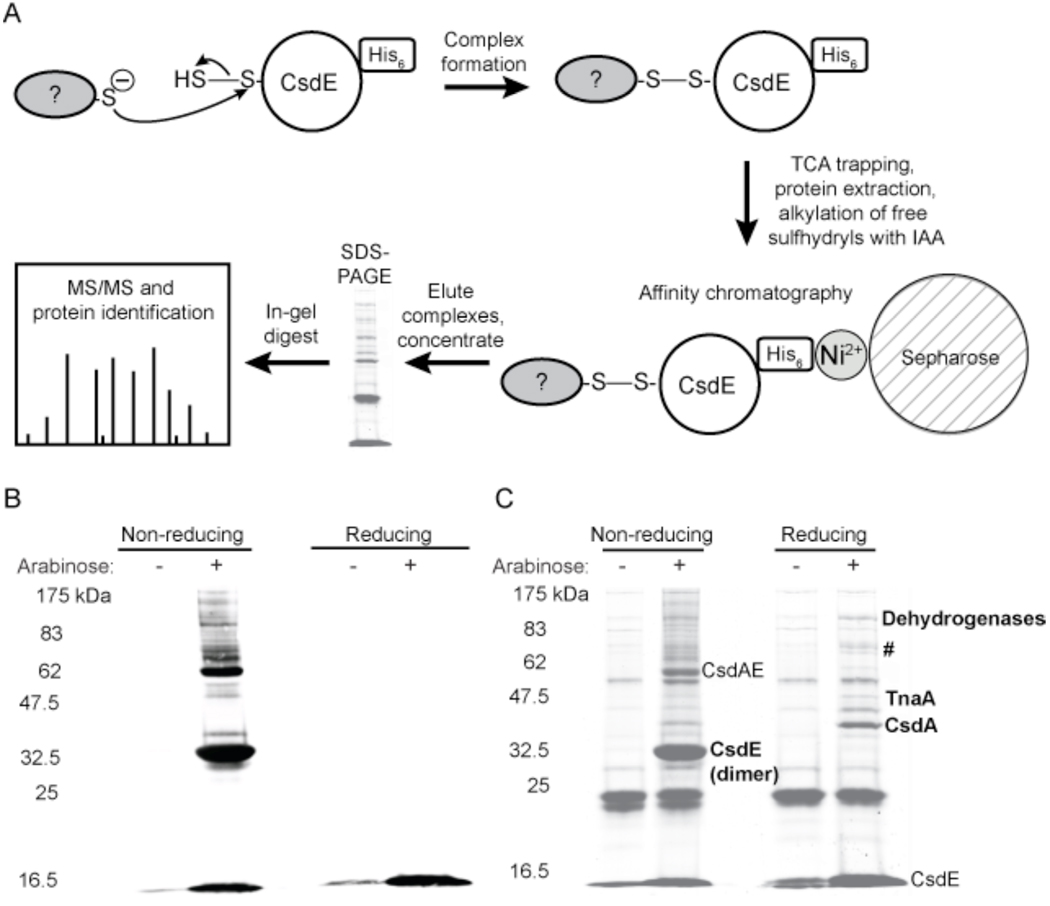
Figure 3. Determination of protein interactions involving CsdE.
A, Schematic representation of the methodology used to trap, purify, and identify protein complexes containing CsdE-(His)6. Disulfide-bound protein complexes form when a cysteine thiol on an interacting protein makes a nucleophilic attack on the bridging sulfur of the CsdE persulfide. Complexes formed within E. coli cells expressing CsdAE-(His)6 are trapped and extracted in the presence of TCA, free sulfhydryls are alkylated with IAA, and the extract is applied to a Ni2+ affinity column. The eluted proteins are concentrated, separated by reducing and nonreducing SDS-PAGE, digested by in-gel proteolysis, and analyzed with either MALDI-TOF/TOF or LC-MS/MS. The mass spectrometry data is searched against an E. coli proteomic database to identify the proteins that interact with CsdE. B and C, characterization of protein complex formation and identification of proteins that interact with CsdE. Arabinose was used to induce protein expression in the CsdAE-(His)6 E. coli strain and protein extracts were prepared as described above, resolved by nonreducing and reducing SDS-PAGE, and then transferred to nitrocellulose for immunoblotting with anti-His6 antibodies (B) or stained for total protein (C). The CsdE monomer is observed at ~15 kDa, and under nonreducing conditions the CsdE dimer can be observed at ~32.5 kDa and the predicted CsdE-CsdA complex can be observed at ~62 kDa. Under nonreducing conditions, complexes containing CsdE are observed in the immunoblot (B). These complexes disappear under reducing conditions, indicating that the complexes are bound by disulfide bonds. When stained for total protein (C), the proteins that copurify with CsdE are observed. These proteins were identified by in-gel digest and MALDI-TOF/TOF mass spectrometry (bold). #=pyruvate dehydrogenase (AceF), threonine-tRNA ligase (ThrS), transketolase 1 (TktA), BolA, YdfW, and Q1RE36_ECOUT. The dehydrogenases include SucA, AdhE, AceE, hypothetical proteins ECs3276, Q8FGG9_ECOL6, Q1RBX2_ECOUT, and Q1RCI6_ECOUT.