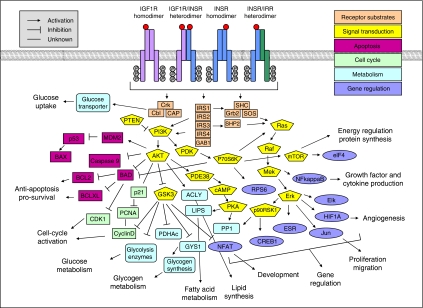
Figure 2.
IGF/INS ligand binding, to one or both receptor monomers, leads to the activation of IGF1R, INSR and IRR, which activate a complex signalling network across the two major signalling pathways PI3K–AKT and RAS–RAF–MAPK (shown here in parts (for detailed signalling networks see Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway database (http://www.genome.jp/keg) and GeneGO pathway analysis database (http://www.genego.com)). The IGF/INS axis regulates multiple functions in normal physiology and pathophysiology. IGF1R and INSR have been reported to act by means of the same pathways. The signal is influenced by different binding velocities, reaction times, activities, expression levels and sub-cellular locations of signalling molecules. Selective substrate specificities for IGF1R and INSR probably also exist.