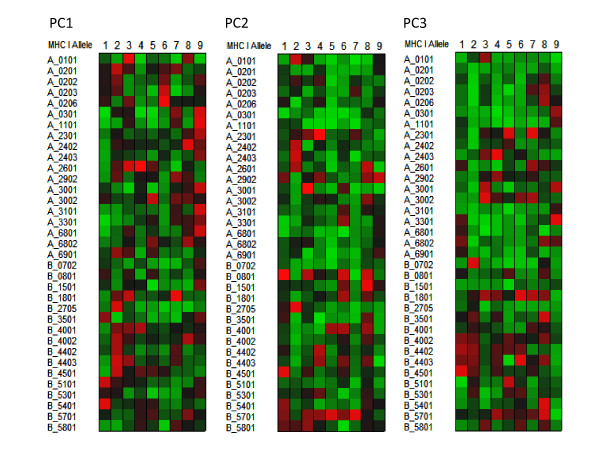
Figure 6.
Visualization of the contribution of the different physical properties of amino acid to the peptide binding to MHC-I. Variable importance projection (VIP) of the PLS regression prediction of ln(ic50) of peptide binding by using the first three principal components of the amino acids in each of the amino acids in the 9-mer as predictors (PC1) Principal component 1, polarity correlate; (PC2) principal compent 2, size correlate, (PC3) principal component 3, electronic correlate. The colors compare the relative importance of the particular numbered residue of the binding domain among the MHC-I alleles indicated. Cells in the matrix with VIP >1 are the most relevant in explaining the binding affinity. Coloration is column-relative for each position in the binding domain (a copy of this figure with details of color scaling can be found in Additional File 8; Figure S6). The particular MHC-I allele in each row is indicated on the left. A 9 amino acid binding domain is shown using the standard for the MHC binding groove numbered N-terminus to C-terminus 1 through 9.